Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice
- PMID: 20018701
- PMCID: PMC2793316
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912139106
Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice
Abstract
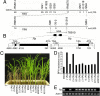
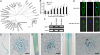
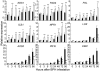
Planthoppers are highly destructive pests in crop production worldwide. Brown planthopper (BPH) causes the most serious damage of the rice crop globally among all rice pests. Growing resistant varieties is the most effective and environment-friendly strategy for protecting the crop from BPH. More than 19 BPH-resistance genes have been reported and used to various extents in rice breeding and production. In this study, we cloned Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to BPH at seedling and maturity stages of the rice plant, using a map-base cloning approach. We show that Bph14 encodes a coiled-coil, nucleotide-binding, and leucine-rich repeat (CC-NB-LRR) protein. Sequence comparison indicates that Bph14 carries a unique LRR domain that might function in recognition of the BPH insect invasion and activating the defense response. Bph14 is predominantly expressed in vascular bundles, the site of BPH feeding. Expression of Bph14 activates the salicylic acid signaling pathway and induces callose deposition in phloem cells and trypsin inhibitor production after planthopper infestation, thus reducing the feeding, growth rate, and longevity of the BPH insects. Our work provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of rice defense against insects and facilitates the development of resistant varieties to control this devastating insect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Normile D. Reinventing rice to feed the world. Science. 2008;321:330–333. 7. - PubMed
-
- Sōgawa K. The rice brown planthopper: Feeding physiology and host plant interactions. Annu Rev Entomol. 1982;27:49–73.
-
- Du PV, et al. Yellowing syndrome of rice: Etiology, current status and future challenges. Omonrice. 2007;15:94–101.
-
- Tanaka K, Endo S, Kazano H. Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice planthoppers: Spiders, the mirid bug and the dryinid wasp. Appl Entomol Zool. 2000;35:177–187.
-
- Khush GS. Green revolution: The way forward. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:815–822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

