The N-terminus of histone H3 is required for de novo DNA methylation in chromatin
- PMID: 20018712
- PMCID: PMC2799746
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0905767106
The N-terminus of histone H3 is required for de novo DNA methylation in chromatin
Abstract
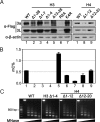
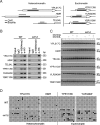
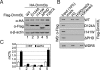
DNA methylation and histone modification are two major epigenetic pathways that interplay to regulate transcriptional activity and other genome functions. Dnmt3L is a regulatory factor for the de novo DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b. Although recent biochemical studies have revealed that Dnmt3L binds to the tail of histone H3 with unmethylated lysine 4 in vitro, the requirement of chromatin components for DNA methylation has not been examined, and functional evidence for the connection of histone tails to DNA methylation is still lacking. Here, we used the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model system to investigate the chromatin determinants of DNA methylation through ectopic expression of murine Dnmt3a and Dnmt3L. We found that the N terminus of histone H3 tail is required for de novo methylation, while the central part encompassing lysines 9 and 27, as well as the H4 tail are dispensable. DNA methylation occurs predominantly in heterochromatin regions lacking H3K4 methylation. In mutant strains depleted of H3K4 methylation, the DNA methylation level increased 5-fold. The methylation activity of Dnmt3a largely depends on the Dnmt3L's PHD domain recognizing the histone H3 tail with unmethylated lysine 4. Functional analysis of Dnmt3L in mouse ES cells confirmed that the chromatin-recognition ability of Dnmt3L's PHD domain is indeed required for efficient methylation at the promoter of the endogenous Dnmt3L gene. These findings establish the N terminus of histone H3 tail with an unmethylated lysine 4 as a chromatin determinant for DNA methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
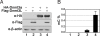

Similar articles
-
Both combinatorial K4me0-K36me3 marks on sister histone H3s of a nucleosome are required for Dnmt3a-Dnmt3L mediated de novo DNA methylation.J Genet Genomics. 2020 Feb 20;47(2):105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2019.12.006. Epub 2020 Feb 21. J Genet Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32173286
-
DNMT3L connects unmethylated lysine 4 of histone H3 to de novo methylation of DNA.Nature. 2007 Aug 9;448(7154):714-7. doi: 10.1038/nature05987. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17687327 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into autoinhibition and histone H3-induced activation of DNMT3A.Nature. 2015 Jan 29;517(7536):640-4. doi: 10.1038/nature13899. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25383530
-
Molecular coupling of DNA methylation and histone methylation.Epigenomics. 2010 Oct;2(5):657-69. doi: 10.2217/epi.10.44. Epigenomics. 2010. PMID: 21339843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular implementation and physiological roles for histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;20(3):341-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.03.019. Epub 2008 May 26. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18508253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Transl Res. 2015 Jan;165(1):48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.03.011. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 24746870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNMT3L enables accumulation and inheritance of epimutations in transgenic Drosophila.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 22;6:19572. doi: 10.1038/srep19572. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26795243 Free PMC article.
-
reChIP-seq reveals widespread bivalency of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in CD4(+) memory T cells.Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 17;7:12514. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12514. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27530917 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics of drug abuse: predisposition or response.Pharmacogenomics. 2012 Jul;13(10):1149-60. doi: 10.2217/pgs.12.94. Pharmacogenomics. 2012. PMID: 22909205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Control of Circadian Clock Operation during Development.Genet Res Int. 2012;2012:845429. doi: 10.1155/2012/845429. Epub 2012 Mar 18. Genet Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22567402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaenisch R, Bird A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Gen. 2003;33:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Bestor TH. The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum Mol Gen. 2000;9:2395–2402. - PubMed
-
- Li E. Chromatin modification and epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:662–673. - PubMed
-
- Tamaru H, Selker EU. A histone H3 methyltransferase controls DNA methylation in Neurospora crassa. Nature. 2001;414:277–283. - PubMed
-
- Lehnertz B, et al. Suv39h-mediated histone H3 lysine 9 methylation directs DNA methylation to major satellite repeats at pericentric heterochromatin. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1192–1200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

