Activation of EGFR on monocytes is required for human cytomegalovirus entry and mediates cellular motility
- PMID: 20018733
- PMCID: PMC2799688
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908787106
Activation of EGFR on monocytes is required for human cytomegalovirus entry and mediates cellular motility
Abstract
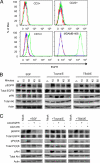
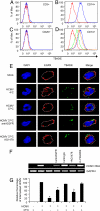
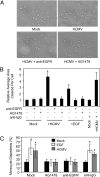
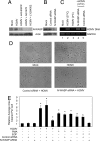
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) rapidly induces a mobile and functionally unique proinflammatory monocyte following infection that is proposed to mediate viral spread. The cellular pathways used by HCMV to initiate these biological changes remain unknown. Here, we document the expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) on the surface of human peripheral blood monocytes but not on other blood leukocyte populations. Inhibition of EGFR signaling abrogated viral entry into monocytes, indicating that EGFR can serve as a cellular tropism receptor. Moreover, HCMV-activated EGFR was required for the induction of monocyte motility and transendothelial migration, two biological events required for monocyte extravasation into peripheral tissue, and thus viral spread. Transcriptome analysis revealed that HCMV-mediated EGFR signaling up-regulated neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP), an actin nucleator whose expression and function are normally limited in leukocytes. Knockdown of N-WASP expression blocked HCMV-induced but not phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced monocyte motility, suggesting that a switch to and/or the distinct use of a new actin nucleator controlling motility occurs during HCMV infection of monocytes. Together, these data provide evidence that EGFR plays an essential role in the immunopathobiology of HCMV by mediating viral entry into monocytes and stimulating the aberrant biological activity that promotes hematogenous dissemination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Toorkey CB, Carrigan DR. Immunohistochemical detection of an immediate early antigen of human cytomegalovirus in normal tissues. J Infect Dis. 1989;160:741–751. - PubMed
-
- Sinzger C, Jahn G. Human cytomegalovirus cell tropism and pathogenesis. Intervirology. 1996;39:302–319. - PubMed
-
- Smith MS, Bentz GL, Smith PM, Bivins ER, Yurochko AD. HCMV activates PI(3)K in monocytes and promotes monocyte motility and transendothelial migration in a PI(3)K-dependent manner. J Leukocyte Biol. 2004;76:65–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

