The SAH domain extends the functional length of the myosin lever
- PMID: 20018767
- PMCID: PMC2794034
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909851106
The SAH domain extends the functional length of the myosin lever
Abstract
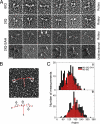
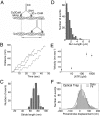
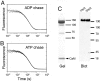
Stable, single alpha-helix (SAH) domains are widely distributed in the proteome, including in myosins, but their functions are unknown. To test whether SAH domains can act as levers, we replaced four of the six calmodulin-binding IQ motifs in the levers of mouse myosin 5a (Myo5) with the putative SAH domain of Dictyostelium myosin MyoM of similar length. The SAH domain was inserted between the IQ motifs and the coiled coil in a Myo5 HMM construct in which the levers were truncated from six to two IQ motifs (Myo5-2IQ). Electron microscopy of this chimera (Myo5-2IQ-SAH) showed the SAH domain was straight and 17 nm long as predicted, restoring the truncated lever to the length of wild-type (Myo5-6IQ). The powerstroke (of 21.5 nm) measured in the optical trap was slightly less than that for Myo5-6IQ but much greater than for Myo5-2IQ. Myo5-2IQ-SAH moved processively along actin at physiological ATP concentrations with similar stride and run lengths to Myo5-6IQ in in-vitro single molecule assays. In comparison, Myo5-2IQ is not processive under these conditions. Solution biochemical experiments indicated that the rear head did not mechanically gate the rate of ADP release from the lead head, unlike Myo5-6IQ. These data show that the SAH domain can form part of a functional lever in myosins, although its mechanical stiffness might be lower. More generally, we conclude that SAH domains can act as stiff structural extensions in aqueous solution and this structural role may be important in other proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Peckham M, Knight PJ. When a predicted coiled coil is really a single α-helix, in myosins and other proteins. Soft Matter. 2009;5:2493–2503.
-
- Mehta AD, et al. Myosin-V is a processive actin-based motor. Nature. 1999;400:590–593. - PubMed
-
- Veigel C, Wang F, Bartoo ML, Sellers JR, Molloy JE. The gated gait of the processive molecular motor, myosin V. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:59–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

