Tonic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- PMID: 20018836
- PMCID: PMC2822683
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00511.2009
Tonic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
Abstract
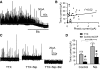
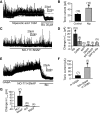
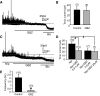
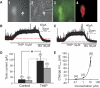
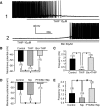
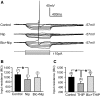
Type A gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA(A)) receptors expressed in the dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (DMV) critically regulate the activity of vagal motor neurons and, by inference, the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Two types of GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition have been identified in the brain, represented by phasic (I(phasic)) and tonic (I(tonic)) inhibitory currents. The hypothesis that I(tonic) regulates neuron activity was tested in the DMV using whole cell patch-clamp recordings in transverse brain stem slices from rats. An I(tonic) was present in a subset of DMV neurons, which was determined to be mediated by different receptors than those mediating fast, synaptic currents. Preapplication of tetrodotoxin significantly decreased the resting I(tonic) amplitude in DMV neurons, suggesting that most of the current was due to action potential (AP)-dependent GABA release. Blocking GABA transport enhanced I(tonic) and multiple GABA transporters cooperated to regulate I(tonic). The I(tonic) was composed of both a gabazine-insensitive component that was nearly saturated under basal conditions and a gabazine-sensitive component that was activated when extracellular GABA concentration was elevated. Perfusion of THIP (10 muM) significantly increased I(tonic) amplitude without increasing I(phasic) amplitude. The I(tonic) played a major role in determining the overall excitability of DMV neurons by contributing to resting membrane potential and AP frequency. Our results indicate that I(tonic) contributes to DMV neuron membrane potential and activity and is thus an important regulator of vagally mediated GI function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GABAA receptor currents in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in females: influence of ovarian cycle and 5α-reductase inhibition.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Nov 1;122(5):2130-2141. doi: 10.1152/jn.00039.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 9. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31596653 Free PMC article.
-
Zolpidem modulation of phasic and tonic GABA currents in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jun;58(8):1220-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.03.003. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 20226798 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and molecular plasticity of γ and α1 GABAA receptor subunits in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus after experimentally induced diabetes.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Nov 1;118(5):2833-2841. doi: 10.1152/jn.00085.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 23. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28835522 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol inhibits pancreatic projecting neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Oct 15;189:121-129. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.08.020. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35998791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiological power of improper tonic GABA(A) conductances in mature and immature models.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Oct 24;7:170. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00170. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 24167475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of epileptiform activity by two distinct subtypes of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors.Mol Brain. 2013 May 1;6:21. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-6-21. Mol Brain. 2013. PMID: 23634821 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental regulation of inhibitory synaptic currents in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in the rat.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Oct 1;116(4):1705-1714. doi: 10.1152/jn.00249.2016. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27440241 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone rapidly increases GABA release in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus via retrograde messenger-mediated enhancement of TRPV1 activity.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 30;8(7):e70505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070505. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936221 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine enhances inhibition of mouse vagal motor neurons by modulating excitability of premotor GABAergic neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarii.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Feb 15;113(4):1165-74. doi: 10.1152/jn.00614.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 26. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25429117 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic ionotropic glutamate receptors modulate GABA release in the mouse dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.Neuroscience. 2015 Nov 12;308:95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.009. Epub 2015 Sep 5. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26343294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai D, Zhu G, Pennefather P, Jackson MF, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of tonic and quantal inhibitory postsynaptic currents mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors in hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol 59: 814–824, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein EM, Quick MW. Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporters by extracellular GABA. J Biol Chem 274: 889–895, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

