The C terminus of the Alb3 membrane insertase recruits cpSRP43 to the thylakoid membrane
- PMID: 20018841
- PMCID: PMC2820820
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.084996
The C terminus of the Alb3 membrane insertase recruits cpSRP43 to the thylakoid membrane
Abstract
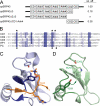
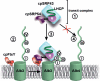
The YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 family of membrane proteins controls the insertion and assembly of membrane proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Here we describe the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction of Alb3 with the chloroplast signal recognition particle (cpSRP). The Alb3 C-terminal domain (A3CT) is intrinsically disordered and recruits cpSRP to the thylakoid membrane by a coupled binding and folding mechanism. Two conserved, positively charged motifs reminiscent of chromodomain interaction motifs in histone tails are identified in A3CT that are essential for the Alb3-cpSRP43 interaction. They are absent in the C-terminal domain of Alb4, which therefore does not interact with cpSRP43. Chromodomain 2 in cpSRP43 appears as a central binding platform that can interact simultaneously with A3CT and cpSRP54. The observed negative cooperativity of the two binding events provides the first insights into cargo release at the thylakoid membrane. Taken together, our data show how Alb3 participates in cpSRP-dependent membrane targeting, and our data provide a molecular explanation why Alb4 cannot compensate for the loss of Alb3. Oxa1 and YidC utilize their positively charged, C-terminal domains for ribosome interaction in co-translational targeting. Alb3 is adapted for the chloroplast-specific Alb3-cpSRP43 interaction in post-translational targeting by extending the spectrum of chromodomain interactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A dynamic cpSRP43-Albino3 interaction mediates translocase regulation of chloroplast signal recognition particle (cpSRP)-targeting components.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 29;285(44):34220-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.160093. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20729200 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction studies between the chloroplast signal recognition particle subunit cpSRP43 and the full-length translocase Alb3 reveal a membrane-embedded binding region in Alb3 protein.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 7;286(40):35187-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.250746. Epub 2011 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21832051 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Physical Interaction Studies Reveal Functional Similarities between ALBINO3 and ALBINO4 in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2015 Oct;169(2):1292-306. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00376. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26265777 Free PMC article.
-
Component interactions, regulation and mechanisms of chloroplast signal recognition particle-dependent protein transport.Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;89(12):965-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.06.020. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20709425 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of SRP-dependent light-harvesting protein transport to the thylakoid membrane in plants.Photosynth Res. 2018 Dec;138(3):303-313. doi: 10.1007/s11120-018-0544-6. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Photosynth Res. 2018. PMID: 29956039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Structural Dynamics within a Signal Recognition Particle Promotes Binding of Protein Targeting Substrates.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 19;290(25):15462-15474. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.624346. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25918165 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic cpSRP43-Albino3 interaction mediates translocase regulation of chloroplast signal recognition particle (cpSRP)-targeting components.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 29;285(44):34220-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.160093. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20729200 Free PMC article.
-
LTD is a protein required for sorting light-harvesting chlorophyll-binding proteins to the chloroplast SRP pathway.Nat Commun. 2011;2:277. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1278. Nat Commun. 2011. PMID: 21505433
-
Protein Targeting Into the Thylakoid Membrane Through Different Pathways.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 12;12:802057. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.802057. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35095563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiolipin occupancy profiles of YidC paralogs reveal the significance of respective TM2 helix residues in determining paralog-specific phenotypes.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Oct 6;10:1264454. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1264454. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37867558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cross B. C., Sinning I., Luirink J., High S. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 255–264 - PubMed
-
- Grudnik P., Bange G., Sinning I. (2009) Biol. Chem. 390, 775–782 - PubMed
-
- Luirink J., von Heijne G., Houben E., de Gier J. W. (2005) Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 59, 329–355 - PubMed
-
- Driessen A. J., Nouwen N. (2008) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 643–667 - PubMed
-
- Yi L., Dalbey R. E. (2005) Mol. Membr. Biol. 22, 101–111 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

