Aquaporin-1 tunes pain perception by interaction with Na(v)1.8 Na+ channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons
- PMID: 20018876
- PMCID: PMC2820815
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.090233
Aquaporin-1 tunes pain perception by interaction with Na(v)1.8 Na+ channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons
Abstract
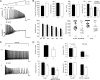
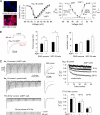
Aquaporin-1 (AQP1) water channels are expressed in the plasma membrane of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. We found reduced osmotic water permeability in freshly isolated DRG neurons from AQP1(-/-) versus AQP1(+/+) mice. Behavioral studies showed greatly reduced thermal inflammatory pain perception in AQP1(-/-) mice evoked by bradykinin, prostaglandin E(2), and capsaicin as well as reduced cold pain perception. Patch clamp of freshly isolated DRG neurons showed reduced action potential firing in response to current injections. Single action potentials after pulse current injections showed reduced maximum inward current, suggesting impaired Na(v)1.8 Na(+) function. Whole-cell Na(v)1.8 Na(+) currents in Na(v)1.8-expressing ND7-23 cells showed slowed frequency-dependent inactivation after AQP1 transfection. Immunoprecipitation studies showed AQP1- Na(v)1.8 Na(+) interaction, which was verified in live cells by single-particle tracking of quantum dot-labeled AQP1. Our results implicate the involvement of AQP1 in DRG neurons for the perception of inflammatory thermal pain and cold pain, whose molecular basis is accounted for, in part, by reduced Na(v)1.8-dependent membrane Na(+) current. AQP1 is, thus, a novel target for pain management.
Figures



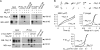

Similar articles
-
Aquaporin-1 water permeability as a novel determinant of axonal regeneration in dorsal root ganglion neurons.Exp Neurol. 2015 Mar;265:152-9. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25585012 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the expression of tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels within dorsal root ganglia neurons in inflammatory pain.Pain. 2004 Apr;108(3):237-247. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2003.12.035. Pain. 2004. PMID: 15030943
-
Chronic exposure to tumor necrosis factor in vivo induces hyperalgesia, upregulates sodium channel gene expression and alters the cellular electrophysiology of dorsal root ganglion neurons.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Jul 13;653:195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 27. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28558976
-
Sodium channels in normal and pathological pain.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010;33:325-47. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153234. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20367448 Review.
-
The trafficking of Na(V)1.8.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Dec 10;486(2):78-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.074. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20816723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Aquaporins: Functional Diversity and Potential Roles in Infectious and Non-infectious Diseases.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 16;12:654865. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.654865. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33796134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporin-1 water permeability as a novel determinant of axonal regeneration in dorsal root ganglion neurons.Exp Neurol. 2015 Mar;265:152-9. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25585012 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of aquaporins in peripheral nervous system.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Jun;32(6):711-5. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.63. Epub 2011 May 23. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 21602841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active shrinkage protects neurons following axonal transection.iScience. 2023 Aug 25;26(10):107715. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107715. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37701578 Free PMC article.
-
A Chimeric NaV1.8 Channel Expression System Based on HEK293T Cell Line.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 6;9:337. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00337. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29686617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papadopoulos M. C., Manley G. T., Krishna S., Verkman A. S. (2004) FASEB J. 18, 1291–1293 - PubMed
-
- Manley G. T., Fujimura M., Ma T., Noshita N., Filiz F., Bollen A. W., Chan P., Verkman A. S. (2000) Nat. Med. 6, 159–163 - PubMed
-
- Auguste K. I., Jin S., Uchida K., Yan D., Manley G. T., Papadopoulos M. C., Verkman A. S. (2007) FASEB J. 21, 108–116 - PubMed
-
- Saadoun S., Papadopoulos M. C., Watanabe H., Yan D., Manley G. T., Verkman A. S. (2005) J. Cell Sci. 118, 5691–5698 - PubMed
-
- Binder D. K., Yao X., Zador Z., Sick T. J., Verkman A. S., Manley G. T. (2006) Glia 53, 631–636 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL73856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK86125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK72517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY13574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK35124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DK086125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EB00415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

