Replication initiation at a distance: determination of the cis- and trans-acting elements of replication origin alpha of plasmid R6K
- PMID: 20018882
- PMCID: PMC2820798
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.067348
Replication initiation at a distance: determination of the cis- and trans-acting elements of replication origin alpha of plasmid R6K
Abstract
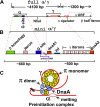
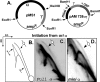
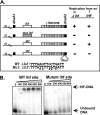
Plasmid R6K, which contains 3 replication origins called alpha, gamma, and beta, is a favorable system to investigate the molecular mechanism(s) of action at a distance, i.e. replication initiation at a considerable distance from the primary initiator protein binding sites (iterons). The centrally located gamma origin contains 7 iterons that bind to the plasmid-encoded initiator protein, pi. Ori alpha, located at a distance of approximately 4 kb from gamma, contains a single iteron that does not directly bind to pi but is believed to access the protein by pi-mediated alpha-gamma iteron-iteron interaction that loops out the intervening approximately 3.7 kb of DNA. Although the cis-acting components and the trans-acting proteins required for ori gamma function have been analyzed in detail, such information was lacking for ori alpha. Here, we have identified both the sequence elements located at alpha and those at gamma, that together promoted alpha activity. The data support the conclusion that besides the single iteron, a neighboring DNA primase recognition element called G site is essential for alpha-directed plasmid maintenance. Sequences preceding the iteron and immediately following the G site, although not absolutely necessary, appear to play a role in efficient plasmid maintenance. In addition, while both dnaA1 and dnaA2 boxes that bind to DnaA protein and are located at gamma were essential for alpha activity, only dnaA2 was required for initiation at gamma. Mutations in the AT-rich region of gamma also abolished alpha function. These results are consistent with the interpretation that a protein-DNA complex consisting of pi and DnaA forms at gamma and activates alpha at a distance by DNA looping.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasmid R6K replication control.Plasmid. 2013 May;69(3):231-42. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Plasmid. 2013. PMID: 23474464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigations of pi initiator protein-mediated interaction between replication origins alpha and gamma of the plasmid R6K.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5695-704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.067439. Epub 2009 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20029091 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of origin activation by monomers of R6K-encoded pi protein.J Mol Biol. 2007 May 11;368(4):928-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.074. Epub 2007 Mar 2. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17383678 Free PMC article.
-
Role of pi dimers in coupling ("handcuffing") of plasmid R6K's gamma ori iterons.J Bacteriol. 2005 Jun;187(11):3779-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.11.3779-3785.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15901701 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory implications of protein assemblies at the gamma origin of plasmid R6K - a review.Gene. 1998 Nov 26;223(1-2):195-204. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00367-9. Gene. 1998. PMID: 9858731 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosomal replication initiation machinery of low-G+C-content Firmicutes.J Bacteriol. 2012 Oct;194(19):5162-70. doi: 10.1128/JB.00865-12. Epub 2012 Jul 13. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22797751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmid R6K replication control.Plasmid. 2013 May;69(3):231-42. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Plasmid. 2013. PMID: 23474464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ptashne M. (2004) Genetic Switch, 3rd Ed., Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
-
- Ma J., Ptashne M. (1988) Cell 55, 443–446 - PubMed
-
- Lobell R. B., Schleif R. F. (1991) J. Mol. Biol. 218, 45–54 - PubMed
-
- Schleif R. (1992) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61, 199–223 - PubMed
-
- Tolhuis B., Palstra R. J., Splinter E., Grosveld F., de Laat W. (2002) Mol. Cell 20, 1453–1465 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

