MicroRNAs regulate human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha, modulating the expression of metabolic enzymes and cell cycle
- PMID: 20018894
- PMCID: PMC2836046
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.085431
MicroRNAs regulate human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha, modulating the expression of metabolic enzymes and cell cycle
Abstract
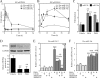
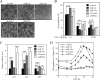
Hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 4alpha is a key transcription factor regulating endo/xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes and transporters. We investigated whether microRNAs are involved in the regulation of human HNF4alpha. Potential recognition elements for miR-24 (MRE24) were identified in the coding region and the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR), and those for miR-34a (MRE34a) were identified in the 3'-UTR in HNF4alpha mRNA. The HNF4alpha protein level in HepG2 cells was markedly decreased by the overexpression of miR-24 and miR-34a. The HNF4alpha mRNA level was significantly decreased by the overexpression of miR-24 but not by miR-34a. In luciferase analyses in HEK293 cells, the reporter activity of plasmid containing the 3'-UTR of HNF4alpha was significantly decreased by miR-34a. The reporter activity of plasmid containing the HNF4alpha coding region downstream of the luciferase gene was significantly decreased by miR-24. These results suggest that the MRE24 in the coding region and MRE34a in the 3'-UTR are functional in the negative regulation by mRNA degradation and translational repression, respectively. The down-regulation of HNF4alpha by these microRNAs resulted in the decrease of various target genes such as cytochrome P450 7A1 and 8B1 as well as morphological changes and the decrease of the S phase population in HepG2 cells. We also clarified that the expressions of miR-24 and miR-34a were regulated by protein kinase C/mitogen-activated protein kinase and reactive oxygen species pathways, respectively. In conclusion, we found that human HNF4alpha was down-regulated by miR-24 and miR-34a, the expression of which are regulated by cellular stress, affecting the metabolism and cellular biology.
Figures


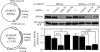
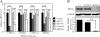

References
-
- Gonzalez F. J. (2008) Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 23, 2–7 - PubMed
-
- Kamiyama Y., Matsubara T., Yoshinari K., Nagata K., Kamimura H., Yamazoe Y. (2007) Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 22, 287–298 - PubMed
-
- Goodwin B., Jones S. A., Price R. R., Watson M. A., McKee D. D., Moore L. B., Galardi C., Wilson J. G., Lewis M. C., Roth M. E., Maloney P. R., Willson T. M., Kliewer S. A. (2000) Mol. Cell 6, 517–526 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

