MMP12, lung function, and COPD in high-risk populations
- PMID: 20018959
- PMCID: PMC2904064
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0904006
MMP12, lung function, and COPD in high-risk populations
Abstract
Background: Genetic variants influencing lung function in children and adults may ultimately lead to the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), particularly in high-risk groups.
Methods: We tested for an association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the gene encoding matrix metalloproteinase 12 (MMP12) and a measure of lung function (prebronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV(1)]) in more than 8300 subjects in seven cohorts that included children and adults. Within the Normative Aging Study (NAS), a cohort of initially healthy adult men, we tested for an association between SNPs that were associated with FEV(1) and the time to the onset of COPD. We then examined the relationship between MMP12 SNPs and COPD in two cohorts of adults with COPD or at risk for COPD.
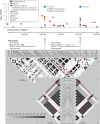
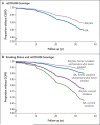
Results: The minor allele (G) of a functional variant in the promoter region of MMP12 (rs2276109 [-82A-->G]) was positively associated with FEV(1) in a combined analysis of children with asthma and adult former and current smokers in all cohorts (P=2x10(-6)). This allele was also associated with a reduced risk of the onset of COPD in the NAS cohort (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46 to 0.92; P=0.02) and with a reduced risk of COPD in a cohort of smokers (odds ratio, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.45 to 0.88; P=0.005) and among participants in a family-based study of early-onset COPD (P=0.006).
Conclusions: The minor allele of a SNP in MMP12 (rs2276109) is associated with a positive effect on lung function in children with asthma and in adults who smoke. This allele is also associated with a reduced risk of COPD in adult smokers.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00000575 NCT00000606.
2009 Massachusetts Medical Society
Figures
Comment in
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 12, asthma, and COPD.N Engl J Med. 2009 Dec 31;361(27):2664-5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe0910626. Epub 2009 Dec 16. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 20018962 No abstract available.
-
MMP12, lung function, and COPD in high-risk populations.N Engl J Med. 2010 Apr 1;362(13):1241; author reply 1242. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1000959. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20357289 No abstract available.
-
MMP12, lung function, and COPD in high-risk populations.N Engl J Med. 2010 Apr 1;362(13):1241; author reply 1242. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20364456 No abstract available.
References
-
- Niewoehner DE, Kleinerman J, Rice DB. Pathologic changes in the peripheral airways of young cigarette smokers. N Engl J Med. 1974;291:755–8. - PubMed
-
- Hautamaki RD, Kobayashi DK, Senior RM, Shapiro SD. Requirement for macrophage elastase for cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. Science. 1997;277:2002–4. - PubMed
-
- Hunninghake GW, Davidson JM, Rennard S, Szapiel S, Gadek JE, Crystal RG. Elastin fragments attract macrophage precursors to diseased sites in pulmonary emphysema. Science. 1981;212:925–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- K08 HL72918/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL083069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL004370/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 HR076113/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076112/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076109/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL66289/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL072918/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076103/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL71393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL065899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076110/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL066289/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076119/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL092222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL075419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL074193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HR076116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- K12 HL089990/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076115/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086601/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL04370/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076106/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
