A comparison of SF-36 and SF-12 composite scores and subsequent hospitalization and mortality risks in long-term dialysis patients
- PMID: 20019120
- PMCID: PMC2827595
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07231009
A comparison of SF-36 and SF-12 composite scores and subsequent hospitalization and mortality risks in long-term dialysis patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: The Short Form 12 (SF-12) has not been validated for long-term dialysis patients. The study compared physical and mental component summary (PCS/MCS) scores from the SF-36 with those from the embedded SF-12 in a national cohort of dialysis patients.
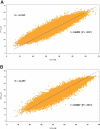
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: All 44,395 patients who had scorable SF-36 and SF-12 from January 1, 2006, to December 31, 2006, and were treated at Fresenius Medical Care, North America facilities were included. Death and first hospitalization were followed for up to 1 year from the date of survey. Correlation and agreement were obtained between PCS-36 and PCS-12 and MCS-36 and MCS-12; then Cox models were constructed to compare associated hazard ratios (HRs) between them.
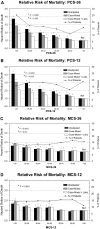
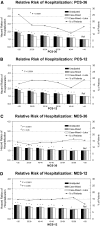
Results: Physical and mental dimensions both exhibited excellent intraclass correlation coefficients of 0.94. Each incremental point for both PCS-12 and PCS-36 was associated with a 2.4% lower adjusted HR of death and 0.4% decline in HR for first hospitalization (both P < 0.0001). Corresponding improvement in HR of death for each MCS point was 1.2% for MCS-12 and 1.3% for MCS-36, whereas both had similar 0.6% lower HR for hospitalization per point (all P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: The use of the SF-12 alone or as part of a larger survey is valid in dialysis patients. Composite scores from the SF-12 and SF-36 have similar prognostic association with death and hospitalization risk. Prospective longitudinal studies of SF-12 surveys that consider responsiveness to specific clinical, situational, and interventional changes are needed in this population.
Figures
References
-
- Ware JE, Snow KS, Kosinski M, Gandek B: SF-36 Health Survey Manual and Interpretation Guide, Boston, The Health Institute, New England Medical Center, 1993
-
- DeOreo PB: Hemodialysis patient-assessed functional health status predicts continued survival, hospitalization, and dialysis-attendance compliance. Am J Kidney Dis 30: 204–212, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Diaz-Buxo JA, Lowrie EG, Lew NL, Zhang H, Lazarus JM: Quality-of-life evaluation using Short Form 36: Comparison in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 35: 293–300, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD, Block G, Humphreys MH: Association among SF36 quality of life measures and nutrition, hospitalization, and mortality in hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 2797–2806, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Lowrie EG, Curtin RB, LePain N, Schatell D: Medical outcomes Study Short Form-36: A consistent and powerful predictor of morbidity and mortality in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 41: 1286–1292, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

