Dickkopf-1 promotes hyperglycemia-induced accumulation of mesangial matrix and renal dysfunction
- PMID: 20019166
- PMCID: PMC2799277
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008101059
Dickkopf-1 promotes hyperglycemia-induced accumulation of mesangial matrix and renal dysfunction
Abstract
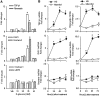
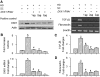
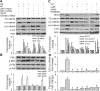
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates renal fibrosis in several model systems including diabetic nephropathy. Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) is an endogenous inhibitor of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, but whether DKK-1 modulates diabetic nephropathy is unknown. Here, we studied whether DKK-1 participates in high glucose (HG)-induced expression of profibrotic factors and renal damage. In vitro, HG increased expression of DKK1, receptor Kremen-2, TGF-beta1, and fibronectin in mesangial cells. Loss and gain of DKK1 function modulated HG-mediated c-Jun, TGF-beta1, and fibronectin expression. DKK1 mediated HG-induced phosphorylation of Ser45-beta-catenin and reduction of nuclear beta-catenin levels, but not phosphorylation of ERK kinase. Wnt3a protein and the beta-catenin (Delta45) mutation increased nuclear beta-catenin but abrogated HG-induced DKK1 and fibronectin expression. Exogenous DKK1 antisense oligonucleotide attenuated the increase in both serum DKK1 and urinary protein excretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Knocking down DKK1 inhibited mesangial expression of TGF-beta1 and fibronectin and reduced both the glomerular volume and deposition of mesangial matrix in diabetic kidneys. Taken together, DKK1 mediates HG-induced destabilization of beta-catenin and matrix accumulation in mesangial cells. Knocking down DKK1 prevents diabetes-induced renal dysfunction and microstructure deterioration, suggesting that inhibition of DKK1offers therapeutic potential for diabetic nephropathy.
Figures

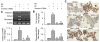

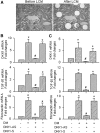

References
-
- Simonson MS: Phenotypic transitions and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 71: 846–854, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Mizuno S, Nakamura T: Suppressions of chronic glomerular injuries and TGF-beta 1 production by HGF in attenuation of murine diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286: F134–F143, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Furlong F, Crean J, Thornton L, O'Leary R, Murphy M, Martin F: Dysregulated intracellular signaling impairs CTGF-stimulated responses in human mesangial cells exposed to high extracellular glucose. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292: F1691–F1700, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Giannico G, Cortes P, Baccora MH, Hassett C, Taube DW, Yee J: Glibenclamide prevents increased extracellular matrix formation induced by high glucose concentration in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292: F57–F65, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Lee EA, Seo JY, Jiang Z, Yu MR, Kwon MK, Ha H, Lee HB: Reactive oxygen species mediate high glucose-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 up-regulation in mesangial cells and in diabetic kidney. Kidney Int 67: 1762–1771, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

