Hypoxia triggers subcellular compartmental redox signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20019331
- PMCID: PMC2856085
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.206334
Hypoxia triggers subcellular compartmental redox signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Rationale: Recent studies have implicated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in regulating hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV), but controversy exists regarding whether hypoxia increases or decreases ROS generation.
Objective: This study tested the hypothesis that hypoxia induces redox changes that differ among subcellular compartments in pulmonary (PASMCs) and systemic (SASMCs) smooth muscle cells.
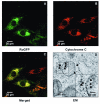
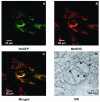
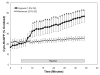
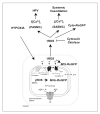
Methods and results: We used a novel, redox-sensitive, ratiometric fluorescent protein sensor (RoGFP) to assess the effects of hypoxia on redox signaling in cultured PASMCs and SASMCs. Using genetic targeting sequences, RoGFP was expressed in the cytosol (Cyto-RoGFP), the mitochondrial matrix (Mito-RoGFP), or the mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS-RoGFP), allowing assessment of oxidant signaling in distinct intracellular compartments. Superfusion of PASMCs or SASMCs with hypoxic media increased oxidation of both Cyto-RoGFP and IMS-RoGFP. However, hypoxia decreased oxidation of Mito-RoGFP in both cell types. The hypoxia-induced oxidation of Cyto-RoGFP was attenuated through the overexpression of cytosolic catalase in PASMCs.
Conclusions: These results indicate that hypoxia causes a decrease in nonspecific ROS generation in the matrix compartment, whereas it increases regulated ROS production in the IMS, which diffuses to the cytosol of both PASMCs and SASMCs.
Figures













Comment in
-
Novel imaging approaches provide new windows to view subcellular changes in the redox state of smooth muscle cells.Circ Res. 2010 Feb 19;106(3):432-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.213660. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20167940 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Archer SL, Nelson DP, Weir EK. Simultaneous measurement of O2 radicals and pulmonary vascular reactivity in rat lung. J Appl Physiol. 1989;67:1903–1911. - PubMed
-
- Archer SL, Huang J, Henry T, Peterson D, Weir EK. A redox-based O2 sensor in rat pulmonary vasculature. Circ Res. 1993;73:1100–1112. - PubMed
-
- Mohazzab KM, Wolin MS. Properties of a superoxide anion-generating microsomal NADH oxidoreductase, a potential pulmonary artery PO2 sensor. Am J Physiol. 1994;267:L823–831. - PubMed
-
- Michelakis ED, Hampl V, Nsair A, Wu X, Harry G, Haromy A, Gurtu R, Archer SL. Diversity in mitochondrial function explains differences in vascular oxygen sensing. Circ Res. 2002;90:1307–1315. - PubMed
-
- Mehta JP, Campian JL, Guardiola J, Cabrera JA, Weir EK, Eaton JW. Generation of oxidants by hypoxic human pulmonary and coronary smooth-muscle cells. Chest. 2008;133:1410–1414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

