Visual Arrestin 1 contributes to cone photoreceptor survival and light adaptation
- PMID: 20019357
- PMCID: PMC2864311
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-4895
Visual Arrestin 1 contributes to cone photoreceptor survival and light adaptation
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate morphologic and functional contributions of Arrestin 1 (Arr1) and Arrestin 4 (Arr4) in cone photoreceptors, the authors examined the phenotypes of visual arrestin knockout mice (Arr1(-/-), Arr4(-/-), Arr1(-/-)Arr4(-/-) [Arr-DKO]) reared in darkness.
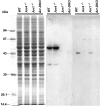
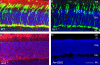
Methods: Retinal rods and cones were evaluated in wild-type (WT), Arr1(-/-), Arr4(-/-), and Arr-DKO mice using quantitative morphologic analysis, immunoblot, immunohistochemistry, TUNEL, and electroretinographic (ERG) techniques.
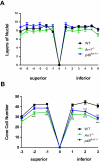
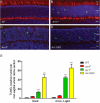
Results: Compared with either Arr4(-/-) or WT, Arr1(-/-) and Arr-DKO mice had increased apoptotic nuclei in their retinal outer nuclear layer (ONL) at postnatal day (P) 22. By P60, cone density was significantly diminished, but the ONL appeared normal. After 1 minute of background illumination, cone ERG b-wave amplitudes were similar in WT and all Arr KO mice. However, by 3 minutes and continuing through 15 minutes of light adaptation, the cone b-wave amplitudes of WT and Arr4(-/-) mice increased significantly over those of the Arr1(-/-) and Arr-DKO mice, which demonstrated no cone b-wave amplitude increase. In contrast, ERG flicker analysis after the 15-minute light adaptation period demonstrated no loss in amplitude for either Arr1(-/-) or Arr4(-/-) mice, whereas Arr-DKO had significantly lower amplitudes. When Arr1 expression was restored in Arr1(-/-) mice (+p48(Arr1-/-)), normal cone density and light-adapted ERG b-wave amplitudes were observed.
Conclusions: In the adult dark-reared Arr1(-/-) and Arr-DKO mice, viable cones diminish over time. Arr1 expression is essential for cone photoreceptor survival and light adaptation, whereas either Arr1 or Arr4 is necessary for maintaining normal flicker responses.
Figures


References
-
- Wacker WB, Lipton MM. Experimental allergic uveitis: homologous retina as uveitogenic antigen. Nature 1965;206:253–254 - PubMed
-
- Wacker WB, Donoso LA, Kalsow CM, Yankeelov JA, Jr, Organisciak DT. Experimental allergic uveitis: isolation, characterization, and localization of a soluble uveitopathogenic antigen from bovine retina. J Immunol 1977;119:1949–1958 - PubMed
-
- Kuhn H. Light-regulated binding of rhodopsin kinase and other proteins to cattle photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry 1978;17:4389–4395 - PubMed
-
- Pfister C, Chabre M, Plouet J, et al. Retinal S antigen identified as the 48K protein regulating light-dependent phosphodiesterase in rods. Science 1985;228:891–893 - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Dodd RL, Makino CL, Simon MI, Baylor DA, Chen J. Prolonged photoresponses in transgenic mouse rods lacking arrestin. Nature 1997;389:505–509 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

