Dose escalation of second-line sunitinib results in rapid partial remission of multiple hepatic metastases
- PMID: 20019964
- PMCID: PMC2792436
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.1190
Dose escalation of second-line sunitinib results in rapid partial remission of multiple hepatic metastases
Abstract
A 58-year-old man with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma on sunitinib therapy, who previously failed on sorafenib, was found to have progression of multiple hepatic metastases; he was on a standard sunitinib dose of 50 mg/day (4 weeks on, 2 weeks off). Due to the unavailability of alternative therapies, a sunitinib dose escalation of 50 mg/day was attempted. After one 6-week cycle of continuously dosed sunitinib 50 mg, the hepatic lesions regressed. After the second cycle, virtual disappearance of the lesions was recorded. There was no added toxicity. These findings suggest that sunitinib dose escalation to 50 mg/day using continuous daily administration dosing might represent a valid, effective and well-tolerated therapeutic option in patients who progress on standard sunitinib therapy.
Figures
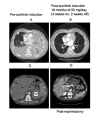
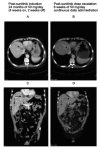
Similar articles
-
Clinical experience with sunitinib dose escalation in metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2015 Sep;11(3):e1-5. doi: 10.1111/ajco.12296. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25560278
-
Dose escalation can maximize therapeutic potential of sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 15;18(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4209-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29544452 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I study of safety and tolerability of sunitinib in combination with sirolimus in patients with refractory solid malignancies and determination of VEGF (VEGF-A) and soluble VEGF-R2 (sVEGFR2) in plasma.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;77(6):1193-200. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3033-7. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27103123 Clinical Trial.
-
[Alternative prescription schedules of sunitinib in metastatic kidney cancer: from the underground to the light?].Bull Cancer. 2014 Sep;101(9):832-40. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2014.2020. Bull Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25295955 Review. French.
-
Alternative dosing schedules for sunitinib as a treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014 Dec;92(3):208-17. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2014.07.006. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014. PMID: 25151214 Review.
Cited by
-
Sunitinib rechallenge with dose escalation in progressive metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(31):e11565. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011565. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30075524 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al. Sunitinib versus Interferon Alfa in Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–24. - PubMed
-
- Dudek AZ, Zolnierek J, Dham A, et al. Sequential Therapy with Sorafenib and Sunitinib in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer. 2009;115:61–7. - PubMed
-
- Tamaskar I, Garcia JA, Elson P, et al. Antitumor Effects of Sunitinib or Sorafenib in Patients with Metastatic Renal Carcinoma Who Received Prior Antiangiogenic Therapy. J Urol. 2008;179:81–6. - PubMed
-
- Heng DY, Rini BI, Garcia J, et al. Prolonged Complete Responses and Near-Complete Responses to Sunitinib in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2007;5:446–51. - PubMed
-
- Amato RJ, Harris P, Dalton M, et al. A phase II trial of intra-patient dose-escalated sorafenib in patients (pts) with metastatic renal cell cancer (MRCC) [abstract] J Clin Oncol 200725abstr 5026.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
