Dominant Mycobacterium tuberculosis lineages in elderly patients born in Norway
- PMID: 20020043
- PMCID: PMC2791218
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008373
Dominant Mycobacterium tuberculosis lineages in elderly patients born in Norway
Abstract
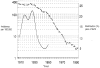
Background: During the previous century Norway had a high incidence of tuberculosis, but no molecular epidemiological studies could be performed and these previously epidemic strains have been disappearing during the last decades. Currently, tuberculosis among native Norwegians is in the elimination phase, and it is still not known what type of M. tuberculosis was so efficiently controlled during the second half of the 20th century. However, many elderly Norwegian-born people still develop TB that cannot be clustered to imported or recently transmitted strains of M. tuberculosis. Thus, the majority of these cases are results of reactivation of disease that was transmitted many decades ago.
Methodology/principal findings: A total of 213 strains of M. tuberculosis isolated during 1998-2005, from patients born in Norway before 1950 were genotyped in the current study. The findings demonstrated a highly homogenous M. tuberculosis population among the patients. A total of 40% belonged to the T-family, were 35% were assigned to T1 sub- family (T2 = 0, 93%, T3 = 1, 4% and T4 = 2, 3%). As many as 35% of the isolates belonged to the Haarlem family, were 15% were assigned to Haarlem1 and 19% to Haarlem3. The remaining 25% belonged to 15 different other families. The RFLP-patterns indicated that the isolates were not a result of recent transmission, but rather represented well established strains that apparently dominated in Norway many decades ago.
Conclusions/significance: The T 1, Haarlem 1, and Haarlem 3 families of M. tuberculosis were abundant among patients born in Norway before 1950. The M. tuberculosis cases represented reactivated disease that had been acquired before 1994 and were likely to have been latent for several decades. Thus, the current study indicated that the T 1, Haarlem 1, and Haarlem 3 families may have been common in Norway, when tuberculosis represented a serious public health threat during the first half of the 20th century.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains potentially involved in the TB epidemic in Sweden a century ago.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046848. Epub 2012 Oct 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056484 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic characterization and historical perspective of Mycobacterium tuberculosis among older and younger Finns, 2008-2011.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014 Nov;20(11):1134-9. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12725. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24944074
-
Spoligotype-based comparative population structure analysis of multidrug-resistant and isoniazid-monoresistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex clinical isolates in Poland.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Nov;48(11):3899-909. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00572-10. Epub 2010 Sep 1. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20810763 Free PMC article.
-
[New era in molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in Japan].Kekkaku. 2006 Nov;81(11):693-707. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17154049 Review. Japanese.
-
[Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using by RFLP analysis between genomic DNA--its accomplishment and practice].Kekkaku. 2003 Oct;78(10):641-51. Kekkaku. 2003. PMID: 14621573 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains potentially involved in the TB epidemic in Sweden a century ago.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046848. Epub 2012 Oct 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056484 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering of tuberculosis cases based on variable-number tandem-repeat typing in relation to the population structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the Netherlands.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Jul;51(7):2427-31. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00489-13. Epub 2013 May 8. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23658260 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex in Jos, Nigeria.BMC Infect Dis. 2010 Jun 26;10:189. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-189. BMC Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20579382 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in Finland, 2008-2011.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 26;8(12):e85027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085027. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malik AN, Godfrey-Faussett P. Effects of genetic variability of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains on the presentation of disease. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2005;5:174–183. - PubMed
-
- Ordway D, Henao-Tamayo M, Harton M, Palanisamy G, Troudt J, et al. The Hypervirulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strain HN878 Induces a Potent TH1 Response followed by Rapid Down-Regulation. J Immunol. 2007;179:522–531. - PubMed
-
- Dahle UR, Eldholm V, Winje BA, Mannsaker T, Heldal E. Impact of Immigration on the Molecular Epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a Low-Incidence Country. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:930–935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

