Normative data for the 12 item WHO Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0
- PMID: 20020047
- PMCID: PMC2791224
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008343
Normative data for the 12 item WHO Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS 2.0) measures disability due to health conditions including diseases, illnesses, injuries, mental or emotional problems, and problems with alcohol or drugs.
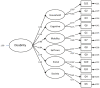
Method: The 12 Item WHODAS 2.0 was used in the second Australian Survey of Mental Health and Well-being. We report the overall factor structure and the distribution of scores and normative data (means and SDs) for people with any physical disorder, any mental disorder and for people with neither.
Findings: A single second order factor justifies the use of the scale as a measure of global disability. People with mental disorders had high scores (mean 6.3, SD 7.1), people with physical disorders had lower scores (mean 4.3, SD 6.1). People with no disorder covered by the survey had low scores (mean 1.4, SD 3.6).
Interpretation: The provision of normative data from a population sample of adults will facilitate use of the WHODAS 2.0 12 item scale in clinical and epidemiological research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rehm J, Ustun TB, Saxena S, Nelson CB, Chatterji S, et al. On the development and psychometric testing of the WHO screening instrument to assess disablement in the general population. Int J Methods in Psychiatric Research. 1999;8:110–122.
-
- Von Korff M, Andrews G, Delves M. Progress in assessing activity limitations and global disability among adults. 2009. Proceedings of the 2009 American Psychopathological Association meetings Mar 5–7; New York City, U.S (in press)
-
- Revicki DA, Irwin D, Reblando J, Simon GE. The accuracy of self-reported disability days. Med Care. 1994;32:401–404. - PubMed
-
- Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Simon D, Liberman J, Von Korff M. Validity of an illness severity measure for headache in a population sample of migraine sufferers. Pain. 1999;79:291–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical