GBR 12909 administration as a mouse model of bipolar disorder mania: mimicking quantitative assessment of manic behavior
- PMID: 20020109
- PMCID: PMC2806531
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-009-1744-8
GBR 12909 administration as a mouse model of bipolar disorder mania: mimicking quantitative assessment of manic behavior
Abstract
Rationale: Mania is a core feature of bipolar disorder (BD) that traditionally is assessed using rating scales. Studies using a new human behavioral pattern monitor (BPM) recently demonstrated that manic BD patients exhibit a specific profile of behavior that differs from schizophrenia and is characterized by increased motor activity, increased specific exploration, and perseverative locomotor patterns as assessed by spatial d.
Objectives: It was hypothesized that disrupting dopaminergic homeostasis by inhibiting dopamine transporter (DAT) function would produce a BD mania-like phenotype in mice as assessed by the mouse BPM.
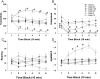
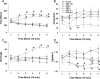
Methods: We compared the spontaneous locomotor and exploratory behavior of C57BL/6J mice treated with the catecholamine transporter inhibitor amphetamine or the selective DAT inhibitor GBR 12909 in the mouse BPM. We also assessed the duration of the effect of GBR 12909 by testing mice in the BPM for 3 h and its potential strain dependency by testing 129/SvJ mice.
Results: Amphetamine produced hyperactivity and increased perseverative patterns of locomotion as reflected in reduced spatial d values but reduced exploratory activity in contrast to the increased exploration observed in BD patients. GBR 12909 increased activity and reduced spatial d in combination with increased exploratory behavior, irrespective of inbred strain. These effects persisted for at least 3 h.
Conclusions: Thus, selectively inhibiting the DAT produced a long-lasting cross-strain behavioral profile in mice that was consistent with that observed in manic BD patients. These findings support the use of selective DAT inhibition in animal models of the impaired dopaminergic homeostasis putatively involved in the pathophysiology of BD mania.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

