The effect of age on the pathogenesis of a highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1 virus in Pekin ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) infected experimentally
- PMID: 20021503
- PMCID: PMC4941950
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2009.00116.x
The effect of age on the pathogenesis of a highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1 virus in Pekin ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) infected experimentally
Abstract
Background: Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1 viruses have recently displayed increased virulence for wild waterfowl.
Objectives: To study the effect of host age on the shedding and tissue dissemination of a HPAI H5N1 virus in infected Pekin ducks.
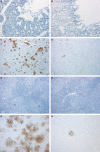
Methods: Pekin ducks in two age-matched groups (n = 18), 8 and 12 weeks old (wo) were each infected with 10(6) EID(50)/0.1 ml of HPAI A/turkey/Turkey/1/05 (H5N1, clade 2.2). Each day for 5 days, birds were monitored clinically, and cloacal and oropharyngeal swabs collected, before three birds from each group were selected randomly for post-mortem examination. Tissue samples were collected for examination by real-time RT-PCR, histopathology and immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Results: Severe clinical signs, including incoordination and torticollis were observed in the 8 wo group resulting in 100% mortality by 4 dpi. Mild clinical signs were observed in the 12 wo group with no mortality. Real-time RT-PCR and IHC results demonstrated the systemic spread of H5N1 virus in birds of both age groups. Higher levels of virus shedding were detected in oropharyngeal swabs than in cloacal swabs, with similar levels of shedding detected in both age groups. Variations in level and temporal dissemination of virus within tissues of older ducks, and the presence of the virus in brain and heart were observed, which coincided with the appearance of clinical signs preceding death in younger birds.
Conclusions: These results are consistent with reports of natural infections of wild waterfowl and poultry possibly indicating an age-related association with dissemination and clinical outcome in ducks following infection with H5N1 HPAI virus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathogenesis of highly pathogenic avian influenza A/turkey/Turkey/1/2005 H5N1 in Pekin ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) infected experimentally.Avian Pathol. 2008 Dec;37(6):619-27. doi: 10.1080/03079450802499126. Avian Pathol. 2008. PMID: 19023759
-
Differences in the detection of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus in feather samples from 4-week-old and 24-week-old infected Pekin ducks (Anas platyrhynchos var. domestica).Vet Microbiol. 2013 Aug 30;165(3-4):443-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.03.019. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23608476
-
Efficacy of a Recombinant Turkey Herpesvirus H5 Vaccine Against Challenge With H5N1 Clades 1.1.2 and 2.3.2.1 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses in Domestic Ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus).Avian Dis. 2016 Mar;60(1):22-32. doi: 10.1637/11282-091615-Reg.1. Avian Dis. 2016. PMID: 26953940
-
Vaccination of domestic ducks against H5N1 HPAI: a review.Virus Res. 2013 Dec 5;178(1):21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.07.012. Epub 2013 Aug 3. Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23916865 Review.
-
H5N1 avian influenza in cats. ABCD guidelines on prevention and management.J Feline Med Surg. 2009 Jul;11(7):615-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jfms.2009.05.011. J Feline Med Surg. 2009. PMID: 19481042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Clinical Manifestation of HPAI H5Nx in Different Poultry Types in the Netherlands, 2014-2022.Pathogens. 2024 Mar 26;13(4):280. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13040280. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38668235 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the PB2 mutation 627K on highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus is dependent on the virus lineage.J Virol. 2013 Sep;87(18):9983-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01399-13. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23843645 Free PMC article.
-
Perpetuation of Avian Influenza from Molt to Fall Migration in Wild Swan Geese (Anser cygnoides): An Agent-Based Modeling Approach.Viruses. 2025 Jan 30;17(2):196. doi: 10.3390/v17020196. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40006951 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of species, breed and route of virus inoculation on the pathogenicity of H5N1 highly pathogenic influenza (HPAI) viruses in domestic ducks.Vet Res. 2013 Jul 22;44(1):62. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-62. Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 23876184 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Dependent Lethality in Ducks Caused by Highly Pathogenic H5N6 Avian Influenza Virus.Viruses. 2020 May 29;12(6):591. doi: 10.3390/v12060591. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32485904 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

