Integrating horizontal gene transfer and common descent to depict evolution and contrast it with "common design"
- PMID: 20021546
- PMCID: PMC4813655
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2009.00458.x
Integrating horizontal gene transfer and common descent to depict evolution and contrast it with "common design"
Abstract
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) and common descent interact in space and time. Because events of HGT co-occur with phylogenetic evolution, it is difficult to depict evolutionary patterns graphically. Tree-like representations of life's diversification are useful, but they ignore the significance of HGT in evolutionary history, particularly of unicellular organisms, ancestors of multicellular life. Here we integrate the reticulated-tree model, ring of life, symbiogenesis whole-organism model, and eliminative pattern pluralism to represent evolution. Using Entamoeba histolytica alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (EhADH2), a bifunctional enzyme in the glycolytic pathway of amoeba, we illustrate how EhADH2 could be the product of both horizontally acquired features from ancestral prokaryotes (i.e. aldehyde dehydrogenase [ALDH] and alcohol dehydrogenase [ADH]), and subsequent functional integration of these enzymes into EhADH2, which is now inherited by amoeba via common descent. Natural selection has driven the evolution of EhADH2 active sites, which require specific amino acids (cysteine 252 in the ALDH domain; histidine 754 in the ADH domain), iron- and NAD(+) as cofactors, and the substrates acetyl-CoA for ALDH and acetaldehyde for ADH. Alternative views invoking "common design" (i.e. the non-naturalistic emergence of major taxa independent from ancestry) to explain the interaction between horizontal and vertical evolution are unfounded.
Figures
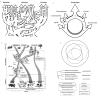

References
-
- Alsmark UC, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Goster PG, Hirt RP, Embley TM. Horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotic parasites: a case study of Entamoeba histolytica and Trichomonas vaginalis. In: Gogarten MB, Gogarten JP, Olendzenski L, editors. Horizontal Gene Transfer: Genomes in Flux. Humana Press; New York: 2009. pp. 489–500. - PubMed
-
- Andersson JO. Eukaryotic gene transfer: adaptation and replacements. In: Hensel M, Schmidt H, editors. Horizontal Gene Transfer in the Evolution of Pathogenesis. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, MA: 2008. pp. 293–315.
-
- Andersson JO. Horizontal gene transfer between microbial eukaryotes. In: Boekels Gogarten M, Gogarten JP, Olendzenski L, editors. Horizontal Gene Transfer: Genomes in Flux. Humana Press; New York: 2009. pp. 473–487.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

