Combined effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms TP53 R72P and MDM2 SNP309, and p53 expression on survival of breast cancer patients
- PMID: 20021639
- PMCID: PMC2815553
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2460
Combined effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms TP53 R72P and MDM2 SNP309, and p53 expression on survival of breast cancer patients
Abstract
Introduction: Somatic inactivation of the TP53 gene in breast tumors is a marker for poor outcome, and breast cancer outcome might also be affected by germ-line variation in the TP53 gene or its regulators. We investigated the effects of the germ-line single nucleotide polymorphisms TP53 R72P (215G>C) and MDM2 SNP309 (-410T>G), and p53 protein expression in breast tumors on survival.
Methods: We pooled data from four breast cancer cohorts within the Breast Cancer Association Consortium for which both TP53 R72P and MDM2 SNP309 were genotyped and follow-up was available (n = 3,749). Overall and breast cancer-specific survival analyses were performed using Kaplan-Meier analysis and multivariate Cox's proportional hazards regression models.
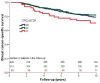
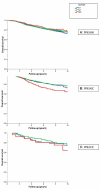
Results: Survival of patients did not differ by carriership of either germ-line variant, R72P (215G>C) or SNP309 (-410G>T) alone. Immunohistochemical p53 staining of the tumor was available for two cohorts (n = 1,109 patients). Survival was worse in patients with p53-positive tumors (n = 301) compared to patients with p53-negative tumors (n = 808); breast cancer-specific survival: HR 1.6 (95% CI 1.2 to 2.1), P = 0.001. Within the patient group with p53-negative tumors, TP53 rare homozygous (CC) carriers had a worse survival than G-allele (GG/GC) carriers; actuarial breast cancer-specific survival 71% versus 80%, P = 0.07; HR 1.8 (1.1 to 3.1), P = 0.03. We also found a differential effect of combinations of the two germ-line variants on overall survival; homozygous carriers of the G-allele in MDM2 had worse survival only within the group of TP53 C-allele carriers; actuarial overall survival (GG versus TT/TG) 64% versus 75%, P = 0.001; HR (GG versus TT) 1.5 (1.1 to 2.0), P = 0.01. We found no evidence for a differential effect of MDM2 SNP309 by p53 protein expression on survival.
Conclusions: The TP53 R72P variant may be an independent predictor for survival of patients with p53-negative tumors. The combined effect of TP53 R72P and MDM2 SNP309 on survival is in line with our a priori biologically-supported hypothesis, that is, the role of enhanced DNA repair function of the TP53 Pro-variant, combined with increased expression of the Mdm2 protein, and thus overall attenuation of the p53 pathway in the tumor cells.
Figures
Comment in
-
Have the roles of two functional polymorphisms in breast cancer, R72P in P53 and MDM2-309 in MDM2, become clearer?Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(1):102. doi: 10.1186/bcr2474. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Breast Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20156327 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Association of the germline TP53 R72P and MDM2 SNP309 variants with breast cancer survival in specific breast tumor subgroups.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130(2):599-608. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1615-y. Epub 2011 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21667122
-
Individual and combined effects of MDM2 SNP309 and TP53 Arg72Pro on breast cancer risk: an updated meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Sep;39(9):9265-74. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1800-z. Epub 2012 Jun 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22729912
-
MDM2 SNP309 and TP53 R72P associated with severe and febrile neutropenia in breast cancer patients treated with 5-FU/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(3):947-53. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1637-5. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21706156
-
A case-control study on the SNP309T → G and 40-bp Del1518 of the MDM2 gene and a systematic review for MDM2 polymorphisms in the patients with breast cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Dec;34(12):e23529. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23529. Epub 2020 Sep 20. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32951271 Free PMC article.
-
TP53 mutations and MDM2 polymorphisms in breast and ovarian cancers: amelioration by drugs and natural compounds.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Jul;27(7):2789-2800. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03841-6. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39797946 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico analysis of polymorphisms in microRNAs that target genes affecting aerobic glycolysis.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Feb;4(4):69. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2016.01.35. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27004216 Free PMC article.
-
Association between MDM2 SNP309, p53 Arg72Pro, and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep;96(36):e7856. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007856. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28885338 Free PMC article.
-
Germline variation in TP53 regulatory network genes associates with breast cancer survival and treatment outcome.Int J Cancer. 2013 May 1;132(9):2044-55. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27884. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23034890 Free PMC article.
-
A functional polymorphism T309G in MDM2 gene promoter, intensified by Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide, is associated with both an increased susceptibility and poor prognosis of gastric carcinoma in Chinese patients.BMC Cancer. 2013 Mar 18;13:126. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-126. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23506213 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: An insight into molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.World J Hepatol. 2012 Dec 27;4(12):342-55. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i12.342. World J Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 23355912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmidt MK, Reincke S, Broeks A, Braaf LM, Hogervorst FBL, Tollenaar RAEM, Johnson N, Fletcher O, Peto J, Tommiska J, Blomqvist C, Nevanlinna HA, Healey CS, Dunning AM, Pharoah PD, Easton DF, Dork T, Van't Veer LJ. on behalf of the Breast Cancer Association Consortium. Do MDM2 SNP309 and TP53 R72P Interact in Breast Cancer Susceptibility? A Large Pooled Series from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9584–9590. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0738. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fagerholm R, Hofstetter B, Tommiska J, Aaltonen K, Vrtel R, Syrjakoski K, Kallioniemi A, Kilpivaara O, Mannermaa A, Kosma VM, Uusitupa M, Eskelinen M, Kataja V, Aittomaki K, von Smitten K, Heikkila P, Lukas J, Holli K, Bartkova J, Blomqvist C, Bartek J, Nevanlinna H. NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 NQO1*2 genotype (P187S) is a strong prognostic and predictive factor in breast cancer. Nat Genet. 2008;40:844–853. doi: 10.1038/ng.155. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

