Assessing the utility of whole-genome amplified serum DNA for array-based high throughput genotyping
- PMID: 20021669
- PMCID: PMC2803178
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-10-85
Assessing the utility of whole-genome amplified serum DNA for array-based high throughput genotyping
Abstract
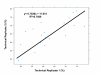
Background: Whole genome amplification (WGA) offers new possibilities for genome-wide association studies where limited DNA samples have been collected. This study provides a realistic and high-precision assessment of WGA DNA genotyping performance from 20-year old archived serum samples using the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 (SNP6.0) platform.
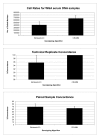
Results: Whole-genome amplified (WGA) DNA samples from 45 archived serum replicates and 5 fresh sera paired with non-amplified genomic DNA were genotyped in duplicate. All genotyped samples passed the imposed QC thresholds for quantity and quality. In general, WGA serum DNA samples produced low call rates (45.00 +/- 2.69%), although reproducibility for successfully called markers was favorable (concordance = 95.61 +/- 4.39%). Heterozygote dropouts explained the majority (>85% in technical replicates, 50% in paired genomic/serum samples) of discordant results. Genotyping performance on WGA serum DNA samples was improved by implementation of Corrected Robust Linear Model with Maximum Likelihood Classification (CRLMM) algorithm but at the loss of many samples which failed to pass its quality threshold. Poor genotype clustering was evident in the samples that failed the CRLMM confidence threshold.
Conclusions: We conclude that while it is possible to extract genomic DNA and subsequently perform whole-genome amplification from archived serum samples, WGA serum DNA did not perform well and appeared unsuitable for high-resolution genotyping on these arrays.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

