Supracricoid partial laryngectomy with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy in patients with radiation therapy failure
- PMID: 20021681
- PMCID: PMC2801667
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-7-101
Supracricoid partial laryngectomy with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy in patients with radiation therapy failure
Abstract
Background: To assess functional results, complications, and success of larynx preservation in patients with recurrent squamous cell carcinoma after radiotherapy.
Methods: From a database of 40 patients who underwent supracricoid partial laryngectomy (SCPL) with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy (CHEP) from June 2001 to April 2006, eight patients were treated previously with radiotherapy due to squamous cell carcinoma of the glottic region and were treated for recurrence at the site of the primary cancer.
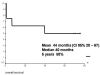
Results: SCPL with CHEP was performed in six men and two women with a mean age of 67 years due to recurrence and/or persistence at a mean time of 30 months postradiotherapy (in case #8 after concomitant chemoradiotherapy). Bilateral neck dissection at levels II-V was performed in six patients. Only case #8 presented metastasis in one node. In case #5, Delphian node was positive. It was possible to preserve both arytenoids in five cases. Definitive surgical margins were negative. Complications were encountered in seven patients. Follow-up was on average 44 months (range: 20-67 months). Organ preservation in this series was 75%, and local control was 87%. Overall 5-year survival was 50%.
Conclusions: In selected patient with persistence and/or recurrence after radiotherapy due to cancer of the larynx, SCPL with CHEP seems to be feasible with acceptable local control and toxicity. Complications may occur as in previously non-irradiated patients. These complications must be treated conservatively to avoid altering laryngeal function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Supracricoid partial laryngectomy as salvage surgery after radiation failure.Head Neck. 2002 Aug;24(8):759-65. doi: 10.1002/hed.10117. Head Neck. 2002. PMID: 12203801
-
[Supracricoid partial laryngectomy as salvage for recurrent carcinoma of the larynx initially treated by vertical partial hemilaryngectomy. Case report].Cir Cir. 2008 Jul-Aug;76(4):333-7. Cir Cir. 2008. PMID: 18778545 Spanish.
-
Induction chemotherapy followed by supracricoid partial laryngectomy (SCPL) with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy (CHEP) in T3NO arytenoid fixation-related glottic cancer.B-ENT. 2016;12(4):271-277. B-ENT. 2016. PMID: 29709130
-
Supracricoid laryngectomy with cricohyoidopexy for recurrence of early-stage glottic carcinoma after irradiation. Long-term oncological and functional results.Acta Otolaryngol. 2005 Jan;125(1):91-5. doi: 10.1080/00016480410017927. Acta Otolaryngol. 2005. PMID: 15799582 Review.
-
Supracricoid partial laryngectomy for radiorecurrent laryngeal cancer: a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Jul;275(7):1671-1680. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-4986-4. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29713885
Cited by
-
Analyses of functional and oncologic outcomes following supracricoid partial laryngectomy.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Nov;272(11):3463-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3363-1. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25359194
-
Supracricoid laryngectomy for recurrent laryngeal cancer after chemoradiotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2016 Dec;36(6):439-449. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1063. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2016. PMID: 28177326 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical management and oncological outcome of non-squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx: a bicentric study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Jan;279(1):299-310. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07076-x. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34557960 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of Delphian lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a single-institution study, systemic review and meta-analysis.J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Aug 30;48(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40463-019-0362-7. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 31470907 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Inhibition of GLUT-1 Expression and the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway to Enhance the Radiosensitivity of Laryngeal Carcinoma Xenografts In Vivo.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 24;10(11):e0143306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143306. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26600164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Small W, Mittal BB, Brand WN, Shetty RM, Rademaker AW, Beck GG, Hoover SV. Results of radiation therapy in early glottic carcinoma. Radiology. 1992;183:789–94. - PubMed
-
- Harwood AR, Hawkins NW, Rider WD, Bryes DP. Radiotherapy of early glottic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979;5:473–6. - PubMed
-
- Woodhouse RJ, Quivey JM, Fu KK, Sien PS, Dedo HH, Phillips TL. Treatment of carcinoma of the vocal cord. A review of 20 years experience. Laryngoscope. 1981;92:1155–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous