TLK1B promotes repair of DSBs via its interaction with Rad9 and Asf1
- PMID: 20021694
- PMCID: PMC2803485
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-110
TLK1B promotes repair of DSBs via its interaction with Rad9 and Asf1
Abstract
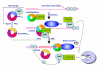
Background: The Tousled-like kinases are involved in chromatin assembly, DNA repair, transcription, and chromosome segregation. Previous evidence indicated that TLK1B can promote repair of plasmids with cohesive ends in vitro, but it was inferred that the mechanism was indirect and via chromatin assembly, mediated by its interaction with the chromatin assembly factor Asf1. We recently identified Rad9 as a substrate of TLK1B, and we presented evidence that the TLK1B-Rad9 interaction plays some role in DSB repair. Hence the relative contribution of Asf1 and Rad9 to the protective effect of TLK1B in DSBs repair is not known. Using an adeno-HO-mediated cleavage system in MM3MG cells, we previously showed that overexpression of either TLK1B or a kinase-dead protein (KD) promoted repair and the assembly of Rad9 in proximity of the DSB at early time points post-infection. This established that it is a chaperone activity of TLK1B and not directly the kinase activity that promotes recruitment of 9-1-1 to the DSB. However, the phosphorylation of Rad9(S328) by TLK1B appeared important for mediating a cell cycle checkpoint, and thus, this phosphorylation of Rad9 may have other effects on 9-1-1 functionality.
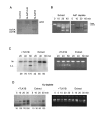
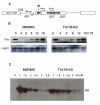
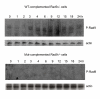
Results: Here we present direct evidence that TLK1B can promote repair of linearized plasmids with incompatible ends that require processing prior to ligation. Immunodepletion of Rad9 indicated that Rad9 was important for processing the ends preceding ligation, suggesting that the interaction of TLK1B with Rad9 is a key mediator for this type of repair. Ligation of incompatible ends also required DNA-PK, as addition of wortmannin or immunodepletion of Ku70 abrogated ligation. Depletion of Ku70 prevented the ligation of the plasmid but did not affect stimulation of the fill-in of the ends by added TLK1B, which was attributed to Rad9. From experiments with the HO-cleavage system, we now show that Rad17, a subunit of the "clamp loader", associates normally with the DSB in KD-overexpressing cells. However, the subsequent release of Rad17 and Rad9 upon repair of the DSB was significantly slower in these cells compared to controls or cells expressing wt-TLK1B.
Conclusions: TLKs play important roles in DNA repair, not only by modulation of chromatin assembly via Asf1, but also by a more direct function in processing the ends of a DSB via interaction with Rad9. Inhibition of Rad9 phosphorylation in KD-overexpressing cells may have consequences in signaling completion of the repair and cell cycle re-entry, and could explain a loss of viability from DSBs in these cells.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

