Serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor reflects adrenal function in the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis of septic patients: an observational study
- PMID: 20021698
- PMCID: PMC2807431
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-209
Serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor reflects adrenal function in the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis of septic patients: an observational study
Abstract
Background: The hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis modulates the inflammatory response during sepsis. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), which counteracts the anti-inflammatory activity of glucocorticoid (GC), is one of the mediators of the development of inflammation. An inflammatory imbalance involving GC and MIF might be the cause or result of adrenal insufficiency. Our objective was to clarify the relationship between serum MIF and adrenal function in the HPA axis of sepsis patients using the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test.
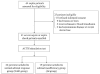
Methods: An observational study was performed in a university intensive care unit over a two-year period. Of 64 consecutive sepsis patients, 41 were enrolled. The enrolled patients underwent an ACTH stimulation test within 24 h of the diagnosis of severe sepsis or septic shock. Clinical and laboratory parameters, including serum MIF and cortisol, were measured.
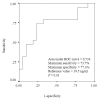
Results: Based on their responses to the ACTH stimulation test, the patients were divided into a normal adrenal response (NAR) group (n = 22) and an adrenal insufficiency (AI) group (n = 19). The AI group had significantly more septic shock patients and higher prothrombin time ratios, serum MIF, and baseline cortisol than did the NAR group (P < 0.05). Serum MIF correlated significantly with the SOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) score, prothrombin time ratio, and delta max cortisol, which is maximum increment of serum cortisol concentration after ACTH stimulation test (rs = 0.414, 0.355, and -0.49, respectively, P < 0.05). Serum MIF also correlated significantly with the delta max cortisol/albumin ratio (rs = -0.501, P = 0.001). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis identified the threshold serum MIF concentration (19.5 ng/mL, P = 0.01) that segregated patients into the NAR and AI groups.
Conclusions: The inverse correlation between serum MIF and delta max cortisol or the delta max cortisol/albumin ratio suggests that high serum MIF reflects an insufficient adrenal response in the HPA axis. Serum MIF could be a valuable clinical marker of adrenal insufficiency in sepsis patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Response of serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor levels to stimulation or suppression of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in normal subjects and patients with Cushing's disease.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Apr;87(4):1834-40. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.4.8382. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 11932327
-
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis of patients with severe sepsis: altered response to corticotropin-releasing hormone.Crit Care Med. 2001 Feb;29(2):310-6. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200102000-00017. Crit Care Med. 2001. PMID: 11246311
-
Association between high levels of blood macrophage migration inhibitory factor, inappropriate adrenal response, and early death in patients with severe sepsis.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 May 15;44(10):1321-8. doi: 10.1086/514344. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17443469 Clinical Trial.
-
Adrenal dysfunction in critically ill children.Minerva Endocrinol. 2014 Dec;39(4):235-43. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Minerva Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25069846 Review.
-
Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal function during critical illness: limitations of current assessment methods.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Oct;91(10):3725-45. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0674. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16882746 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in sepsis: meta-analysis of clinical trials.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 13;11(1):8051. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87613-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33850259 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) and D-Dopachrome Tautomerase (D-DT/MIF-2) in Infections: A Clinical Perspective.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 19;12(1):2. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010002. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38275363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct patterns of serum and urine macrophage migration inhibitory factor kinetics predict death in sepsis: a prospective, observational clinical study.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 11;13(1):588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27506-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36631486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vincent JL, Bernard GR, Beale R, Doig C, Putensen C, Dhainaut JF, Artigas A, Fumagalli R, Macias W, Wright T, Wong K, Sundin DP, Turlo MA, Janes J. Drotrecogin alfa (activated) treatment in severe sepsis from the global open-label trial ENHANCE: Further evidence for survival and safety and implications for early treatment. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:2266–2277. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000181729.46010.83. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vinsonneau C, Camus C, Combes A, Costa de Beauregard MA, Klouche K, Pallot JL, Chiche JD, Taupin P, Landais P, Dhainaut JF. Continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration versus intermittent haemodialysis for acute renal failure in patients with multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2006;368:379–385. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69111-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

