A 3D-structural model of unsulfated chondroitin from high-field NMR: 4-sulfation has little effect on backbone conformation
- PMID: 20022001
- PMCID: PMC3098369
- DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2009.11.013
A 3D-structural model of unsulfated chondroitin from high-field NMR: 4-sulfation has little effect on backbone conformation
Abstract
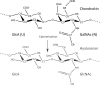
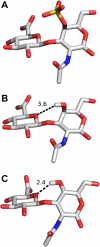
The glycosaminoglycan chondroitin sulfate is essential in human health and disease but exactly how sulfation dictates its 3D-structure at the atomic level is unclear. To address this, we have purified homogenous oligosaccharides of unsulfated chondroitin (with and without (15)N-enrichment) and analysed them by high-field NMR to make a comparison published chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronan 3D-structures. The result is the first full assignment of the tetrasaccharide and an experimental 3D-model of the hexasaccharide (PDB code 2KQO). In common with hyaluronan, we confirm that the amide proton is not involved in strong, persistent inter-residue hydrogen bonds. However, in contrast to hyaluronan, a hydrogen bond is not inferred between the hexosamine OH-4 and the glucuronic acid O5 atoms across the beta(1-->3) glycosidic linkage. The unsulfated chondroitin bond geometry differs slightly from hyaluronan by rotation about the beta(1-->3) psi dihedral (as previously predicted by simulation), while the beta(1-->4) linkage is unaffected. Furthermore, comparison shows that this glycosidic linkage geometry is similar in chondroitin-4-sulfate. We therefore hypothesise that both hexosamine OH-4 and OH-6 atoms are solvent exposed in chondroitin, explaining why it is amenable to sulfation and hyaluronan is not, and also that 4-sulfation has little effect on backbone conformation. Our conclusions exemplify the value of the 3D-model presented here and progress our understanding of glycosaminoglycan molecular properties.
2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structures of Streptococcus pneumoniae hyaluronate lyase in complex with chondroitin and chondroitin sulfate disaccharides. Insights into specificity and mechanism of action.J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 12;278(50):50596-606. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307596200. Epub 2003 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 14523022
-
Influence of sulfate and carboxylate groups on the conformation of chondroitin sulfate related disaccharides.Carbohydr Res. 1993 May 7;243(2):225-58. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(93)87031-m. Carbohydr Res. 1993. PMID: 8348541
-
A fingerprinting method for chondroitin/dermatan sulfate and hyaluronan oligosaccharides.Glycobiology. 2000 Apr;10(4):393-401. doi: 10.1093/glycob/10.4.393. Glycobiology. 2000. PMID: 10764827
-
A physiological function of serum proteoglycan bikunin: the chondroitin sulfate moiety plays a central role.Glycoconj J. 2002 May-Jun;19(4-5):241-7. doi: 10.1023/A:1025331929373. Glycoconj J. 2002. PMID: 12975601 Review.
-
Biotechnological advances in the synthesis of modified chondroitin towards novel biomedical applications.Biotechnol Adv. 2023 Oct;67:108185. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108185. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Biotechnol Adv. 2023. PMID: 37290584 Review.
Cited by
-
Sulfation and cation effects on the conformational properties of the glycan backbone of chondroitin sulfate disaccharides.J Phys Chem B. 2015 May 21;119(20):6063-73. doi: 10.1021/jp511431q. Epub 2015 May 7. J Phys Chem B. 2015. PMID: 25906376 Free PMC article.
-
PolySac3DB: an annotated data base of 3 dimensional structures of polysaccharides.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Nov 14;13:302. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-302. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23151233 Free PMC article.
-
Proteoglycans and their heterogeneous glycosaminoglycans at the atomic scale.Biomacromolecules. 2015 Mar 9;16(3):951-61. doi: 10.1021/bm5018386. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Biomacromolecules. 2015. PMID: 25645947 Free PMC article.
-
Carbohydrate force fields.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci. 2012 Jul;2(4):652-697. doi: 10.1002/wcms.89. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 25530813 Free PMC article.
-
In-Depth Molecular Dynamics Study of All Possible Chondroitin Sulfate Disaccharides Reveals Key Insight into Structural Heterogeneity and Dynamism.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 5;12(1):77. doi: 10.3390/biom12010077. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35053225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imberty A., Lortat-Jacob H., Perez S. Carbohydr. Res. 2007;342:430–439. - PubMed
-
- Bishop J.R., Schuksz M., Esko J.D. Nature. 2007;446:1030–1037. - PubMed
-
- Gama C.I., Tully S.E., Sotogaku N., Clark P.M., Rawat M., Vaidehi N., Goddard W.A., 3rd, Nishi A., Hsieh-Wilson L.C. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006;2:467–473. - PubMed
-
- Raman R., Sasisekharan V., Sasisekharan R. Chem. Biol. 2005;12:267–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

