Hepatitis C and interferon induced thyroiditis
- PMID: 20022216
- PMCID: PMC2835812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2009.11.008
Hepatitis C and interferon induced thyroiditis
Abstract
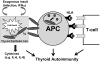
Autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITDs) are complex diseases that develop as a result of interactions between genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. Significant progress has been made in our understanding of the genetic and environmental triggers contributing to AITD. The major environmental triggers of AITD include iodine, smoking, medications, pregnancy, and possibly stress. In this review we will focus on two well-documented environmental triggers of AITD, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and interferon alpha (IFNa) therapy. Chronic HCV infection has been shown to be associated with increased incidence of clinical and subclinical autoimmune thyroiditis (i.e. the presence of thyroid antibodies in euthyroid subjects). Moreover, IFNa therapy of chronic HCV infection is associated with subclinical or clinical thyroiditis in up to 40% of cases which can be autoimmune, or non-autoimmune thyroiditis. In some cases interferon induced thyroiditis (IIT) in chronic HCV patients may result in severe symptomatology necessitating discontinuation of therapy. While the epidemiology and clinical presentation of HCV and interferon induced thyroiditis have been well characterized, the mechanisms causing these conditions are still poorly understood.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Brix TH, Kyvik KO, Christensen K, Hegedus L. Evidence for a major role of heredity in Graves’ disease: a population- based study of two Danish twin cohorts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(2):930–934. - PubMed
-
- Rose NR, Bonita R, Burek CL. Iodine: an environmental trigger of thyroiditis. Autoimmun Rev. 2002;1(1–2):97–103. - PubMed
-
- Li HS, Jiang HY, Carayanniotis G. Modifying effects of iodine on the immunogenicity of thyroglobulin peptides. J Autoimmun. 2007;28(4):171–176. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheim Y, Ban Y, Tomer Y. Interferon induced Autoimmune Thyroid Disease (AITD): a model for human autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2004;3(5):388–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

