Dose-response effects of betamethasone on maturation of the fetal sheep lung
- PMID: 20022315
- PMCID: PMC2815247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.09.033
Dose-response effects of betamethasone on maturation of the fetal sheep lung
Abstract
Objective: Glucocorticoid administration to women in preterm labor improves neonatal mortality and morbidity. Fetal exposure to glucocorticoid levels higher than those appropriate to the current gestational stage has multiple organ system effects. Some, eg, fetal hypertension, are maximal at lower than the clinical dose. We hypothesized that the clinical dose has supramaximal lung maturational effects.
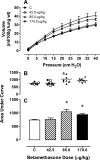
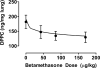
Study design: We evaluated the full, half, and quarter clinical betamethasone dose (12 mg/70 kg or 170 microg/kg intramuscularly twice 24 hours apart) on fetal sheep lung pressure volume curves (PVC) after 48 hours' exposure at 0.75 gestation. We measured key messenger RNAs and protein products that affect lung function and total lung dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl choline.
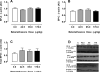
Results: Full and half doses had similar PVC and total lung dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl choline effects. Messenger RNA for surfactant proteins A, B, and D and elastin increased in a dose-dependent fashion.
Conclusion: Half the clinical betamethasone dose produces maximal PVC improvement in fetal sheep at 0.75 gestation.
Copyright 2010 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
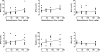
References
-
- Lorenz JM, Wooliever DE, Jetton JR, Paneth N. A Quantitative Review of Mortality and Developmental Disability in Extremely Premature Newborns. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998;152:425–35. - PubMed
-
- NIH Consensus development panel on the effect of corticosteroids for fetal maturation on perinatal outcomes. JAMA. 1995;273:413–18. - PubMed
-
- Leviton LC, Goldenberg RL, Baker CS, Schwartz RM, Freda MC, Fish LJ, et al. Methods to encourage the use of antenatal corticosteroid therapy for fetal maturation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999;281:46–52. - PubMed
-
- Tanswell AK, Byrne PJ, Han RN, Edelson JD, Han VK. Limited division of low-density adult rat type II pneumocytes in serum-free culture. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 1991;260:L395–L402. - PubMed
-
- Willet KE, McMenamin P, Pinkerton KE, Ikegami M, Jobe AH, Gurrin L, et al. Lung Morphometry and Collagen and Elastin Content: Changes During Normal Development and After Prenatal Hormone Exposure in Sheep. Pediatr.Res. 1999;45(5):615–625. Part 1 of 2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

