Stimulation of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx requires MTA1 coregulator
- PMID: 20022949
- PMCID: PMC2844147
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.065987
Stimulation of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx requires MTA1 coregulator
Retraction in
-
Stimulation of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein-HBx requires MTA1 coregulator.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 17;292(11):4765. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A117.065987. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28314778 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Stimulation of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx requires MTA1 coregulator.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 15;291(3):1198. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A109.065987. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26773124 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
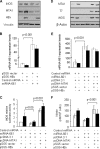
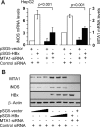
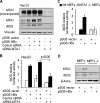
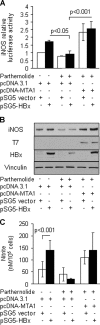
Nitric oxide has been implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders, including hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Transactivator protein HBx, a major regulator of cellular responses of hepatitis B virus, is known to induce the expression of MTA1 (metastasis-associated protein 1) coregulator via NF-kappaB signaling in hepatic cells. However, the underlying mechanism of HBx regulation of the inducible nitric-oxide synthase (iNOS) pathway remains unknown. Here we provide evidence that MTA1 is a positive regulator of iNOS transcription and plays a mechanistic role in HBx stimulation of iNOS expression and activity. We found that the HBx-MTA1 complex is recruited onto the human iNOS promoter in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Pharmacological inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling prevented the ability of HBx to stimulate the transcription, the expression, and the activity of iNOS; nevertheless, these effects could be substantially rescued by MTA1 dysregulation. We further discovered that HBx-mediated stimulation of MTA1 is paralleled by the suppression of miR-661, a member of the small noncoding RNAs, recently shown to target MTA1. We observed that miR-661 controls of MTA1 expression contributed to the expression and activity of iNOS in HBx-expressing HepG2 cells. Accordingly, depletion of MTA1 by either miR-661 or siRNA in HBx-expressing cells severely impaired the ability of HBx to modulate the endogenous levels of iNOS and nitrite production. Together, these findings reveal an inherent role of MTA1 in HBx regulation of iNOS expression and consequently its function in the liver cancer cells.
Figures
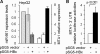

Similar articles
-
NF-kappaB signaling mediates the induction of MTA1 by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx.Oncogene. 2010 Feb 25;29(8):1179-89. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.404. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20010875 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein regulates hepatic glucose homeostasis via activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 26;286(34):29872-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.259978. Epub 2011 Jun 20. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21690090 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx requires MTA1 coregulator.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 15;291(3):1198. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A109.065987. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26773124 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes UV-induced apoptosis by transcriptional transactivation of Fas ligand gene expression.IUBMB Life. 2005 Sep;57(9):651-8. doi: 10.1080/15216540500239697. IUBMB Life. 2005. PMID: 16203685 Review.
-
Regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene in glial cells.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006 May-Jun;8(5-6):929-47. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.929. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006. PMID: 16771683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MTA1 coregulation of transglutaminase 2 expression and function during inflammatory response.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 4;286(9):7132-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.199273. Epub 2010 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21156794 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hepatitis B virus DNA integration in human hepatocarcinogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 May 28;20(20):6236-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6236. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24876744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide: perspectives and emerging studies of a well known cytotoxin.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Jul 16;11(7):2715-45. doi: 10.3390/ijms11072715. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20717533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Biological Function of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Oncol Res. 2019 Mar 29;27(4):509-514. doi: 10.3727/096504018X15278771272963. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 29891022 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections.Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):25087-102. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7837. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26943571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huo T. I., Lee S. D., Wu J. C. (2004) Gastroenterology 127, 360–361; author reply 361–362 - PubMed
-
- Kubicka S., Rudolph K. L., Hanke M., Tietze M. K., Tillmann H. L., Trautwein C., Manns M. (2000) Liver 20, 312–318 - PubMed
-
- Ezzat S., Abdel-Hamid M., Eissa S. A., Mokhtar N., Labib N. A., El-Ghorory L., Mikhail N. N., Abdel-Hamid A., Hifnawy T., Strickland G. T., Loffredo C. A. (2005) Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 208, 329–339 - PubMed
-
- Donato F., Boffetta P., Puoti M. (1998) Int. J. Cancer 75, 347–354 - PubMed
-
- Slagle B. L., Lee T. H., Medina D., Finegold M. J., Butel J. S. (1996) Mol. Carcinog. 15, 261–269 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

