Identification of a novel inhibitor of coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1)-mediated methylation of histone H3 Arg-17
- PMID: 20022955
- PMCID: PMC2844164
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.063933
Identification of a novel inhibitor of coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1)-mediated methylation of histone H3 Arg-17
Abstract
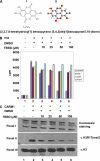
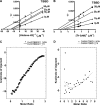
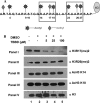
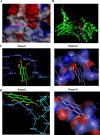
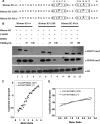
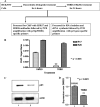
Methylation of the arginine residues of histones by methyltransferases has important consequences for chromatin structure and gene regulation; however, the molecular mechanism(s) of methyltransferase regulation is still unclear, as is the biological significance of methylation at particular arginine residues. Here, we report a novel specific inhibitor of coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1; also known as PRMT4) that selectively inhibits methylation at arginine 17 of histone H3 (H3R17). Remarkably, this plant-derived inhibitor, called TBBD (ellagic acid), binds to the substrate (histone) preferentially at the signature motif, "KAPRK," where the proline residue (Pro-16) plays a critical role for interaction and subsequent enzyme inhibition. In a promoter-specific context, inhibition of H3R17 methylation represses expression of p21, a p53-responsive gene, thus implicating a possible role for H3 Arg-17 methylation in tumor suppressor function. These data establish TBBD as a novel specific inhibitor of arginine methylation and demonstrate substrate sequence-directed inhibition of enzyme activity by a small molecule and its physiological consequence.
Figures
References
-
- Kim S., Park G. H., Paik W. K. (1998) Amino Acids 15, 291–306 - PubMed
-
- Lee D. Y., Teyssier C., Strahl B. D., Stallcup M. R. (2005) Endocr. Rev. 26, 147–170 - PubMed
-
- Bedford M. T., Richard S. (2005) Mol. Cell. 18, 263–272 - PubMed
-
- Schurter B. T., Koh S. S., Chen D., Bunick G. J., Harp J. M., Hanson B. L., Henschen-Edman A., Mackay D. R., Stallcup M. R., Aswad D. W. (2001) Biochemistry 40, 5747–5756 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

