Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death by ATF4 in neuroectodermal tumor cells
- PMID: 20022965
- PMCID: PMC2825403
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014092
Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death by ATF4 in neuroectodermal tumor cells
Abstract
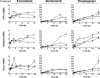
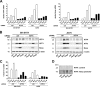
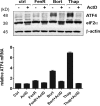
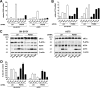
The neuroectodermal tumors neuroblastoma and melanoma represent biologically aggressive and chemoresistant cancers. The chemotherapeutic agents fenretinide and bortezomib induce apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in these tumor types. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that the early events of ER stress signaling and response pathways induced by fenretinide and bortezomib are mediated by the eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha (eIF2alpha)-ATF4 signaling pathway. Treatment of neuroblastoma and melanoma cell lines with fenretinide, bortezomib, or thapsigargin resulted in induction of eIF2alpha signaling, characterized by increased expression of phosphorylated eIF2alpha, ATF4, ATF3, and GADD34. These events correlated with induction of the pro-apoptotic protein Noxa. The cytotoxic response, characterized by up-regulation of Noxa and cell death, was dependent on ATF4, but not the ER-related pro-death signaling pathways involving GADD153 or IRE1. Although PERK-dependent phosphorylation of eIF2alpha enhanced ATF4 protein levels during ER stress, cell death in response to fenretinide, bortezomib, or thapsigargin was not abrogated by inhibition of eIF2alpha phosphorylation through PERK knockdown or overexpression of wild-type eIF2alpha. Furthermore, ATF4 induction in response to ER stress was dependent primarily on transcriptional activation, which occurred in a PERK- and phosphorylated eIF2alpha-independent manner. These results demonstrate that ATF4 mediates ER stress-induced cell death of neuroectodermal tumor cells in response to fenretinide or bortezomib. Understanding the complex regulation of cell death pathways in response to ER stress-inducing drugs has the potential to reveal novel therapeutic targets, thus allowing the development of improved treatment strategies to overcome chemoresistance.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong J. L., Veal G. J., Redfern C. P., Lovat P. E. (2007) Apoptosis 12, 613–622 - PubMed
-
- Brignole C., Marimpietri D., Pastorino F., Nico B., Di Paolo D., Cioni M., Piccardi F., Cilli M., Pezzolo A., Corrias M. V., Pistoia V., Ribatti D., Pagnan G., Ponzoni M. (2006) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 98, 1142–1157 - PubMed
-
- Qin J. Z., Xin H., Sitailo L. A., Denning M. F., Nickoloff B. J. (2006) Cancer Res. 66, 9636–9645 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

