The nonphosphorylative Entner-Doudoroff pathway in the thermoacidophilic euryarchaeon Picrophilus torridus involves a novel 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate- specific aldolase
- PMID: 20023024
- PMCID: PMC2812977
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01281-09
The nonphosphorylative Entner-Doudoroff pathway in the thermoacidophilic euryarchaeon Picrophilus torridus involves a novel 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate- specific aldolase
Abstract
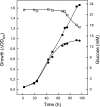
The pathway of glucose degradation in the thermoacidophilic euryarchaeon Picrophilus torridus has been studied by in vivo labeling experiments and enzyme analyses. After growth of P. torridus in the presence of [1-(13)C]- and [3-(13)C]glucose, the label was found only in the C-1 and C-3 positions, respectively, of the proteinogenic amino acid alanine, indicating the exclusive operation of an Entner-Doudoroff (ED)-type pathway in vivo. Cell extracts of P. torridus contained all enzyme activities of a nonphosphorylative ED pathway, which were not induced by glucose. Two key enzymes, gluconate dehydratase (GAD) and a novel 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate (KDG)-specific aldolase (KDGA), were characterized. GAD is a homooctamer of 44-kDa subunits, encoded by Pto0485. KDG aldolase, KDGA, is a homotetramer of 32-kDa subunits. This enzyme was highly specific for KDG with up to 2,000-fold-higher catalytic efficiency compared to 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDPG) and thus differs from the bifunctional KDG/KDPG aldolase, KD(P)GA of crenarchaea catalyzing the conversion of both KDG and KDPG with a preference for KDPG. The KDGA-encoding gene, kdgA, was identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry (MS) as Pto1279, and the correct translation start codon, an ATG 24 bp upstream of the annotated start codon of Pto1279, was determined by N-terminal amino acid analysis. The kdgA gene was functionally overexpressed in Escherichia coli. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that KDGA is only distantly related to KD(P)GA, both enzymes forming separate families within the dihydrodipicolinate synthase superfamily. From the data we conclude that P. torridus degrades glucose via a strictly nonphosphorylative ED pathway with a novel KDG-specific aldolase, thus excluding the operation of the branched ED pathway involving a bifunctional KD(P)GA as a key enzyme.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insights into the Substrate Specificity of Archaeal Entner-Doudoroff Aldolases: The Structures of Picrophilus torridus 2-Keto-3-deoxygluconate Aldolase and Sulfolobus solfataricus 2-Keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate Aldolase in Complex with 2-Keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate.Biochemistry. 2018 Jul 3;57(26):3797-3806. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00535. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29812914
-
Characterization of glycerate kinase (2-phosphoglycerate forming), a key enzyme of the nonphosphorylative Entner-Doudoroff pathway, from the thermoacidophilic euryarchaeon Picrophilus torridus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006 Jun;259(1):113-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00264.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16684110
-
Glyceraldehyde dehydrogenases from the thermoacidophilic euryarchaeota Picrophilus torridus and Thermoplasma acidophilum, key enzymes of the non-phosphorylative Entner-Doudoroff pathway, constitute a novel enzyme family within the aldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily.FEBS Lett. 2006 Feb 20;580(5):1198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.029. Epub 2006 Jan 19. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16458304
-
Crystal structure and stereochemical studies of KD(P)G aldolase from Thermoproteus tenax.Proteins. 2008 Jul;72(1):35-43. doi: 10.1002/prot.21890. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 18186475
-
Key Enzymes of the Semiphosphorylative Entner-Doudoroff Pathway in the Haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii: Characterization of Glucose Dehydrogenase, Gluconate Dehydratase, and 2-Keto-3-Deoxy-6-Phosphogluconate Aldolase.J Bacteriol. 2016 Jul 28;198(16):2251-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.00286-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27297879 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
d-Ribose Catabolism in Archaea: Discovery of a Novel Oxidative Pathway in Haloarcula Species.J Bacteriol. 2020 Jan 15;202(3):e00608-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00608-19. Print 2020 Jan 15. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31712277 Free PMC article.
-
Diterpene Ginkgolides Exert an Antidepressant Effect Through the NT3-TrkA and Ras-MAPK Pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Mar 31;14:1279-1294. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S229145. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32308365 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of NADP+-specific L-rhamnose dehydrogenase from the thermoacidophilic Archaeon Thermoplasma acidophilum.Extremophiles. 2012 May;16(3):447-54. doi: 10.1007/s00792-012-0444-1. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Extremophiles. 2012. PMID: 22481639
-
Optimization of a reduced enzymatic reaction cascade for the production of L-alanine.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 13;9(1):11754. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48151-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31409820 Free PMC article.
-
A physiological perspective on the origin and evolution of photosynthesis.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018 Mar 1;42(2):205-231. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux056. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29177446 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angelov, A., O. Fütterer, O. Valerius, G. H. Braus, and W. Liebl. 2005. Properties of the recombinant glucose/galactose dehydrogenase from the extreme thermoacidophile, Picrophilus torridus. FEBS J. 272:1054-1062. - PubMed
-
- Budgen, N., and M. J. Danson. 1986. Metabolism of glucose via a modified Entner-Doudoroff pathway in the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. FEBS Lett. 196:207-210.
-
- Danson, M. J., and D. W. Hough. 2005. Promiscuity in the Archaea. The enzymology of metabolic pathways. The Biochemist 27:17-21.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

