A mariner-based transposon system for in vivo random mutagenesis of Clostridium difficile
- PMID: 20023081
- PMCID: PMC2820977
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02525-09
A mariner-based transposon system for in vivo random mutagenesis of Clostridium difficile
Abstract
Understanding the molecular basis of Clostridium difficile infection is a prerequisite to the development of effective countermeasures. Although there are methods for constructing gene-specific mutants of C. difficile, currently there is no effective method for generating libraries of random mutants. In this study, we developed a novel mariner-based transposon system for in vivo random mutagenesis of C. difficile R20291, the BI/NAP1/027 epidemic strain at the center of the C. difficile outbreaks in Stoke Mandeville, United Kingdom, in 2003 to 2004 and 2004 to 2005. Transposition occurred at a frequency of 4.5 (+/-0.4) x 10(-4) per cell to give stable insertions at random genomic loci, which were defined only by the nucleotide sequence TA. Furthermore, mutants with just a single transposon insertion were generated in an overwhelming majority (98.3% in this study). Phenotypic screening of a C. difficile R20291 random mutant library yielded a sporulation/germination-defective clone with an insertion in the germination-specific protease gene cspBA and an auxotroph with an insertion in the pyrimidine biosynthesis gene pyrB. These results validate our mariner-based transposon system for use in forward genetic studies of C. difficile.
Figures
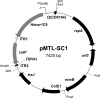


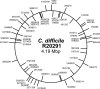
References
-
- Azeddoug, H., J. Hubert, and G. Reysset. 1992. Stable inheritance of shuttle vectors based on plasmid pIM13 in a mutant strain of Clostridium acetobutylicum. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138:1371-1378. - PubMed
-
- Collins, M. E., J. D. Oultram, and M. Young. 1985. Identification of restriction fragments from two cryptic Clostridium butyricum plasmids that promote the establishment of a replication-defective plasmid in Bacillus subtilis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131:2097-2105. - PubMed
-
- Dupuy, B., and A. L. Sonenshein. 1998. Regulated transcription of Clostridium difficile toxin genes. Mol. Microbiol. 27:107-120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

