High heterogeneity within methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 isolates, defined by Cfr9I macrorestriction-pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles and spa and SCCmec types
- PMID: 20023093
- PMCID: PMC2813030
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01721-09
High heterogeneity within methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 isolates, defined by Cfr9I macrorestriction-pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles and spa and SCCmec types
Abstract
During recent years, the animal-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone ST398 has extensively been studied. The DNA of these isolates turned out to be refractory to SmaI restriction, and consequently, SmaI is unsuitable for subtyping this clone by standard pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Very recently, ST398 DNA was shown to be digested by Cfr9I, a neoschizomer of SmaI. In the present study, we employed Cfr9I PFGE on 100 German and 5 Dutch ST398 isolates and compared their PFGE profiles, protein A gene variable repeat regions (spa types), and types of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec). The isolates (from healthy carrier pigs, clinical samples from pigs, dust from farms, milk, and meat) were assigned to 35 profiles, which were correlated to the SCCmec type. A dendrogram with the Cfr9I patterns assigned all profiles to two clusters. Cluster A grouped nearly all isolates with SCCmec type V, and cluster B comprised all SCCmec type IVa and V* (a type V variant first identified as III) carriers plus one isolate with SCCmec type V. Both clusters also grouped methicillin-susceptible S. aureus isolates. The association of the majority of isolates with SCCmec type V in one large cluster indicated the presence of a successful subclone within the clonal complex CC398 from pigs, which has diversified. In general, the combination of Cfr9I PFGE with spa and SCCmec typing demonstrated the heterogeneity of the series analyzed and can be further used for outbreak investigations and traceability studies of the MRSA ST398 emerging clone.
Figures
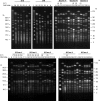
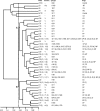
References
-
- Anonymous. 2008. Commission Decision 2008/55/EC concerning a financial contribution of the Community towards a survey on the prevalence of Salmonella spp. and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in herds of breeding pigs to be carried out in the Member States. Off. J. Eur. Union. http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:014:0010:....
-
- Anonymous. 2009. Joint scientific report of ECDC, EFSA and EMEA on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in livestock, companion animals and food. www.health.gov.mt/fsc/fschome_files/efsa_biohaz_report_301_joint_mrsa_en....
-
- Argudín, M. A., M. R. Rodicio, and B. Guerra. 2009. The emerging methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 clone can easily be typed using Cfr9I SmaI neoschizomer. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 50:127-130. - PubMed
-
- Bens, C. C. P. M., A. Voss, and C. H. W. Klaassen. 2006. Presence of a novel DNA methylation enzyme in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with pig farming leads to uninterpretable results in standard pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:1875-1876. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

