Muscarinic receptor-mediated bronchoconstriction is coupled to caveolae in murine airways
- PMID: 20023174
- PMCID: PMC2867404
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00261.2009
Muscarinic receptor-mediated bronchoconstriction is coupled to caveolae in murine airways
Abstract
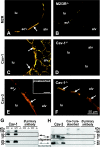
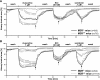
Cholinergic bronchoconstriction is mediated by M(2) and M(3) muscarinic receptors (MR). In heart and urinary bladder, MR are linked to caveolin-1 or -3, the structural proteins of caveolae. Caveolae are cholesterol-rich, omega-shaped invaginations of the plasma membrane. They provide a scaffold for multiple G protein receptors and membrane-bound enzymes, thereby orchestrating signaling into the cell interior. Hence, we hypothesized that airway MR signaling pathways are coupled to caveolae as well. To address this issue, we determined the distribution of caveolin isoforms and MR subtype M2R in murine and human airways and investigated protein-protein associations by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) analysis in immunolabeled murine tissue sections. Bronchoconstrictor responses of murine bronchi were recorded in lung-slice preparations before and after caveolae disruption by methyl-β-cyclodextrin, with efficiency of this treatment being validated by electron microscopy. KCl-induced bronchoconstriction was unaffected after treatment, demonstrating functional integrity of the smooth muscle. Caveolae disruption decreased muscarine-induced bronchoconstriction in wild-type and abolished it in M2R(-/-) and M3R(-/-) mice. Thus M2R and M3R signaling pathways require intact caveolae. Furthermore, we identified a presumed skeletal and cardiac myocyte-specific caveolin isoform, caveolin-3, in human and murine bronchial smooth muscle and found it to be associated with M2R in situ. In contrast, M2R was not associated with caveolin-1, despite an in situ association of caveolin-1 and caveolin-3 that was detected. Here, we demonstrated that M2R- and M3R-mediated bronchoconstriction is caveolae-dependent. Since caveolin-3 is directly associated with M2R, we suggest caveolin-3 as novel regulator of M2R-mediated signaling.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Activation of the SPHK/S1P signalling pathway is coupled to muscarinic receptor-dependent regulation of peripheral airways.Respir Res. 2005 May 31;6(1):48. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-48. Respir Res. 2005. PMID: 15927078 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of muscarinic M2 and M3 receptor signaling in gastrointestinal smooth muscle by caveolin-1.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Aug 1;305(3):C334-47. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00334.2012. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23784544 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic M₃ receptors contribute to allergen-induced airway remodeling in mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 Apr;50(4):690-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0220OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24156289
-
Caveolae and caveolin isoforms in rat peritoneal macrophages.Micron. 2002;33(1):75-93. doi: 10.1016/s0968-4328(00)00100-1. Micron. 2002. PMID: 11473817 Review.
-
The Caveolin genes: from cell biology to medicine.Ann Med. 2004;36(8):584-95. doi: 10.1080/07853890410018899. Ann Med. 2004. PMID: 15768830 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased PDE5 activity and decreased Rho kinase and PKC activities in colonic muscle from caveolin-1-/- mice impair the peristaltic reflex and propulsion.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Dec;305(12):G964-74. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00165.2013. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24157969 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 and force regulation in porcine airway smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Jun;300(6):L920-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00322.2010. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21421751 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Actions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastric, Pancreatic, and Colon Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 5;22(23):13153. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313153. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling the Role of Post-Junctional M2 Muscarinic Receptors in Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contractions of Airway Smooth Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 6;26(12):5455. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125455. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1: Functional Insights into Its Role in Muscarine- and Serotonin-Induced Smooth Muscle Constriction in Murine Airways.Front Physiol. 2017 May 15;8:295. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00295. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28555112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhatnagar A, Sheffler DJ, Kroeze WK, Compton-Toth B, Roth BL. Caveolin-1 interacts with 5-HT2A serotonin receptors and profoundly modulates the signaling of selected Galphaq-coupled protein receptors. J Biol Chem 279: 34614–34623, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Capozza F, Cohen AW, Cheung MW, Sotgia F, Schubert W, Battista M, Lee H, Frank PG, Lisanti MP. Muscle-specific interaction of caveolin isoforms: differential complex formation between caveolins in fibroblastic vs. muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288: C677–C691, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Chilvers ER, Nahorski SR. Phosphoinositide metabolism in airway smooth muscle. Am Rev Respir Dis 141: S137–S140, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Coulson FR, Fryer AD. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and airway diseases. Pharmacol Ther 98: 59–69, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Dreja K, Voldstedlund M, Vinten J, Tranum-Jensen J, Hellstrand P, Sward K. Cholesterol depletion disrupts caveolae and differentially impairs agonist-induced arterial contraction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22: 1267–1272, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

