Class I alpha-mannosidases are required for N-glycan processing and root development in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 20023195
- PMCID: PMC2814498
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.072363
Class I alpha-mannosidases are required for N-glycan processing and root development in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
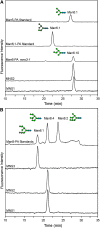
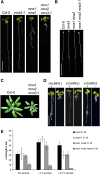
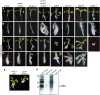
In eukaryotes, class I alpha-mannosidases are involved in early N-glycan processing reactions and in N-glycan-dependent quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). To investigate the role of these enzymes in plants, we identified the ER-type alpha-mannosidase I (MNS3) and the two Golgi-alpha-mannosidase I proteins (MNS1 and MNS2) from Arabidopsis thaliana. All three MNS proteins were found to localize in punctate mobile structures reminiscent of Golgi bodies. Recombinant forms of the MNS proteins were able to process oligomannosidic N-glycans. While MNS3 efficiently cleaved off one selected alpha1,2-mannose residue from Man(9)GlcNAc(2), MNS1/2 readily removed three alpha1,2-mannose residues from Man(8)GlcNAc(2). Mutation in the MNS genes resulted in the formation of aberrant N-glycans in the mns3 single mutant and Man(8)GlcNAc(2) accumulation in the mns1 mns2 double mutant. N-glycan analysis in the mns triple mutant revealed the almost exclusive presence of Man(9)GlcNAc(2), demonstrating that these three MNS proteins play a key role in N-glycan processing. The mns triple mutants displayed short, radially swollen roots and altered cell walls. Pharmacological inhibition of class I alpha-mannosidases in wild-type seedlings resulted in a similar root phenotype. These findings show that class I alpha-mannosidases are essential for early N-glycan processing and play a role in root development and cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.
Figures





Comment in
-
Mannose trimming reactions in the early stages of the N-glycan processing pathway.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Apr;5(4):476-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.4.11423. Epub 2010 Apr 4. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20383064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bencúr, P., Steinkellner, H., Svoboda, B., Mucha, J., Strasser, R., Kolarich, D., Hann, S., Köllensperger, G., Glössl, J., Altmann, F., and Mach, L. (2005). Arabidopsis thaliana beta1,2-xylosyltransferase: An unusual glycosyltransferase with the potential to act at multiple stages of the plant N-glycosylation pathway. Biochem. J. 388 515–525. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burn, J., Hurley, U., Birch, R., Arioli, T., Cork, A., and Williamson, R. (2002). The cellulose-deficient Arabidopsis mutant rsw3 is defective in a gene encoding a putative glucosidase II, an enzyme processing N-glycans during ER quality control. Plant J. 32 949–960. - PubMed
-
- Bush, M.S., and McCann, M.C. (1999). Pectic epitopes are differentially distributed in the cell walls of potato (Solanum tuberosum) tubers. Physiol. Plant. 107 201–213.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

