Effect of neutrophil adhesion on the mechanical properties of lung microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 20023207
- PMCID: PMC2970856
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0381OC
Effect of neutrophil adhesion on the mechanical properties of lung microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
Neutrophil adhesion to pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (ECs) initiates intracellular signaling, resulting in remodeling of F-actin cytoskeletal structure of ECs. The present study determined the mechanical properties of ECs and the changes induced by neutrophil adhesion by atomic force microscopy. The elastic moduli of ECs were compared before neutrophils were present, as soon as neutrophil adhesion was detected, and 1 minute later. ECs that were adjacent to those with adherent neutrophils were also evaluated. Neutrophil adhesion induced a decrease in the elastic moduli in the 6.25-μm rim of ECs surrounding adherent neutrophils as soon as firmly adherent neutrophils were detected, which was transient and lasted less than 1 minute. Adjacent ECs developed an increase in stiffness that was significant in the central regions of these cells. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 crosslinking did not induce significant changes in the elastic modulus of ECs in either region, suggesting that crosslinking intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is not sufficient to induce the observed changes. Our results demonstrate that neutrophil adhesion induces regional changes in the stiffness of ECs.
Figures




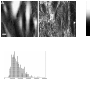

References
-
- Wang Q, Chiang ET, Lim M, Lai J, Rogers R, Janmey PA, Shepro D, Doerschuk CM. Changes in the biomechanical properties of neutrophils and endothelial cells during adhesion. Blood 2001;97:660–668. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, Doerschuk CM. Neutrophil-induced changes in the biomechanical properties of endothelial cells: roles of ICAM-1 and reactive oxygen species. J Immunol 2000;164:6487–6494. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, Yerukhimovich M, Gaarde WA, Popoff IJ, Doerschuk CM. Mkk3 and -6–dependent activation of p38alpha MAP kinase is required for cytoskeletal changes in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells induced by ICAM-1 ligation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2005;288:L359–L369. - PubMed
-
- Marchant RE, Kang I, Sit PS, Zhou Y, Todd BA, Eppell SJ, Lee I. Molecular views and measurements of hemostatic processes using atomic force microscopy. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2002;3:249–274. - PubMed
-
- Radmacher M. Measuring the elastic properties of living cells by the atomic force microscope. Methods Cell Biol 2002;68:67–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

