Simulation study of spatial resolution and sensitivity for the tapered depth of interaction PET detectors for small animal imaging
- PMID: 20023331
- PMCID: PMC3136367
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/2/N04
Simulation study of spatial resolution and sensitivity for the tapered depth of interaction PET detectors for small animal imaging
Abstract
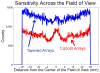
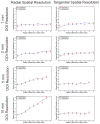
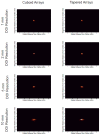
Improvements to current small animal PET scanners can be made by improving the sensitivity and the spatial resolution of the scanner. In the past, efforts have been made to minimize the crystal dimensions in the axial and transaxial directions to improve the spatial resolution and to increase the crystal length to improve the sensitivity of the scanner. We have designed tapered PET detectors with the purpose of reducing the gaps between detector modules and optimizing the sensitivity of a future-generation small animal PET scanner. In this work, we investigate spatial resolution and sensitivity of a scanner based on tapered detector elements using Monte Carlo simulations. For tapered detector elements more scintillation material is used per detector resulting in a higher sensitivity of the scanner. However, since the detector elements are not uniform in size, degradation in spatial resolution is also expected. To investigate characteristics of tapered PET detectors, the spatial resolution and sensitivity of a one-ring scanner were simulated for a system based on traditional cuboid detectors and a scanner based on tapered detectors. Additionally, the effect of depth of interaction (DOI) resolution on the spatial resolution for the traditional and tapered detectors was evaluated. All simulations were performed using the Monte Carlo simulation package GATE. Using the tapered arrays, a 64% improvement in the sensitivity across the field of view was found compared with traditional detectors for the same ring diameter. The level of DOI encoding was found to be the dominating factor in determining the radial spatial resolution and not the detector shape. For all levels of DOI encoding, no significant difference was found for the spatial resolution when comparing the tapered and the cuboid detectors. Detectors employing the tapered crystal design along with excellent DOI resolution will lead to PET scanners with higher sensitivity and uniform spatial resolution across the field of view.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Experimental characterization and system simulations of depth of interaction PET detectors using 0.5 mm and 0.7 mm LSO arrays.Phys Med Biol. 2009 Jul 21;54(14):4605-19. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/14/015. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Phys Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19567945 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of system geometry and other physical factors on photon sensitivity of high-resolution positron emission tomography.Phys Med Biol. 2007 Jul 7;52(13):3753-72. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/52/13/007. Epub 2007 May 29. Phys Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17664575 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of spatial resolution improvement by use of a mouth-insert detector in the helmet PET scanner.Radiol Phys Technol. 2018 Mar;11(1):7-12. doi: 10.1007/s12194-017-0425-2. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Radiol Phys Technol. 2018. PMID: 28986818
-
Recent development in PET instrumentation.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010 Sep 1;11(6):555-71. doi: 10.2174/138920110792246555. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20497121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in PET detector technology.Phys Med Biol. 2008 Sep 7;53(17):R287-317. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/53/17/R01. Epub 2008 Aug 11. Phys Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18695301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Monte Carlo investigation of the spatial resolution performance of a small-animal PET scanner designed for mouse brain imaging studies.Phys Med. 2014 Feb;30(1):76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Phys Med. 2014. PMID: 23566478 Free PMC article.
-
Shared-photodetector readout to improve the sensitivity of positron emission tomography.Phys Med Biol. 2018 Oct 9;63(20):205002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aae056. Phys Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30204125 Free PMC article.
-
Small-animal molecular imaging methods.J Nucl Med. 2010 May 1;51 Suppl 1(0 1):18S-32S. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.068148. J Nucl Med. 2010. PMID: 20457793 Free PMC article.
-
A high resolution and high detection efficiency depth-encoding detector for brain positron emission tomography based on a 0.75 mm pitch scintillator array.J Instrum. 2021 May;16(5):P05015. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/16/05/p05015. Epub 2021 May 20. J Instrum. 2021. PMID: 34925535 Free PMC article.
-
H2RSPET: a 0.5 mm resolution high-sensitivity small-animal PET scanner, a simulation study.Phys Med Biol. 2021 Mar 9;66(6):065016. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/abe558. Phys Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33571980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cesca N, Auricchio N, Di Domenico G, Zavattini G, Malaguti R, Andritschke R, Kanbach G, Schopper F. SiliPET: Design of an ultra-high resolution small animal PET scanner based on stacks of semi-conductor detectors. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2007;572:225–7.
-
- Funk T, Sun M, Hasegawa BH. Radiation dose estimate in small animal SPECT and PET. Med Phys. 2004;31:2680–6. - PubMed
-
- Ishii K, Kikuchi Y, Matsuyama S, Kanai Y, Kotani K, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Funaki Y, Iwata R, Itoh M, Yanai K, Hatazawa J, Itoh N, Tanizaki N, Amano D, Yamada M, Yamaguchi T. First achievement of less than 1 mm FWHM resolution in practical semiconductor animal PET scanner. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2007;576:435–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
