Generation of stable monoclonal antibody-producing B cell receptor-positive human memory B cells by genetic programming
- PMID: 20023635
- PMCID: PMC2861345
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2071
Generation of stable monoclonal antibody-producing B cell receptor-positive human memory B cells by genetic programming
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Generation of stable monoclonal antibody-producing B cell receptor-positive human memory B cells by genetic programming.Nat Med. 2016 Dec 6;22(12):1502. doi: 10.1038/nm1216-1502a. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27923028 No abstract available.
Abstract
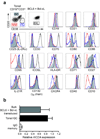
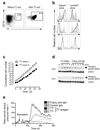
The B cell lymphoma-6 (Bcl-6) and Bcl-xL proteins are expressed in germinal center B cells and enable them to endure the proliferative and mutagenic environment of the germinal center. By introducing these genes into peripheral blood memory B cells and culturing these cells with two factors produced by follicular helper T cells, CD40 ligand (CD40L) and interleukin-21 (IL-21), we convert them to highly proliferating, cell surface B cell receptor (BCR)-positive, immunoglobulin-secreting B cells with features of germinal center B cells, including expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID). We generated cloned lines of B cells specific for respiratory syncytial virus and used these cells as a source of antibodies that effectively neutralized this virus in vivo. This method provides a new tool to study B cell biology and signal transduction through antigen-specific B cell receptors and for the rapid generation of high-affinity human monoclonal antibodies.
Figures
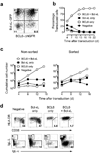
 ), AM16 (○), and AM23 (
), AM16 (○), and AM23 ( )
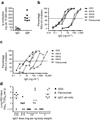
compared to palivizumab (Δ). (c) Neutralization dose response curve of the RSV antibodies D25, AM14, AM16, AM23 and palivizumab against the primary RSV isolate X. Symbols as in 4b (d) Effects of rD25 (●), palivizumab (Δ) and a control IgG1 (×) on RSV replication in cotton rat lungs. Antibodies were administered i.m. one day before intranasal challenge with RSV X (106 TCID50/animal). Lung virus titers were calculated per gram of lung tissue; control prophylaxis reached a titer of 4.7 log TCID50 g−1, while the lower limit of detection was 2.1 log10TCID50 g−1.
)
compared to palivizumab (Δ). (c) Neutralization dose response curve of the RSV antibodies D25, AM14, AM16, AM23 and palivizumab against the primary RSV isolate X. Symbols as in 4b (d) Effects of rD25 (●), palivizumab (Δ) and a control IgG1 (×) on RSV replication in cotton rat lungs. Antibodies were administered i.m. one day before intranasal challenge with RSV X (106 TCID50/animal). Lung virus titers were calculated per gram of lung tissue; control prophylaxis reached a titer of 4.7 log TCID50 g−1, while the lower limit of detection was 2.1 log10TCID50 g−1.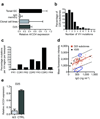
References
-
- Close PM, Pringle JH, Ruprai AK, West KP, Lauder I. Zonal distribution of immunoglobulin-synthesizing cells within the germinal centre: an in situ hybridization and immunohistochemical study. J Pathol. 1990;162:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Liu YJ, Arpin C. Germinal center development. Immunol Rev. 1997;156:111–126. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu M, et al. Specific expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a novel member of the RNA-editing deaminase family in germinal center B cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18470–18476. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu M, et al. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell. 2000;102:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Allen CD, Okada T, Tang HL, Cyster JG. Imaging of germinal center selection events during affinity maturation. Science. 2007;315:528–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

