Activity in the amygdala elicited by unfair divisions predicts social value orientation
- PMID: 20023652
- PMCID: PMC3145100
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2468
Activity in the amygdala elicited by unfair divisions predicts social value orientation
Abstract
'Social value orientation' characterizes individual differences in anchoring attitudes toward the division of resources. Here, by contrasting people with prosocial and individualistic orientations using functional magnetic resonance imaging, we demonstrate that degree of inequity aversion in prosocials is predictable from amygdala activity and unaffected by cognitive load. This result suggests that automatic emotional processing in the amygdala lies at the core of prosocial value orientation.
Figures
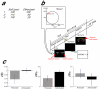
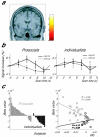
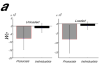
Comment in
-
Amongst equals.Nat Neurosci. 2010 Feb;13(2):151. doi: 10.1038/nn0210-151. Nat Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20104208 No abstract available.
References
-
- Van Lange PAM. J personality and social psychology. 1999;77:337–349.
-
- Bogaert S, Boone C, Declerck C. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2008;43:457–480. - PubMed
-
- Knoch D, Fehr E. Ann. NY. Acad. Sci. 2007;1104:123–134. - PubMed
-
- Haidt J. Psychological Review. 2001;108:814–834. - PubMed
-
- Sanfey AG, Rilling JK, Aronson JA, Nystrom LE, Cohen JD. Science. 2003;300:1755–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

