A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain
- PMID: 20023653
- PMCID: PMC2840225
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2467
A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain
Abstract
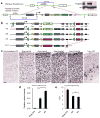
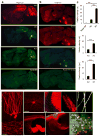
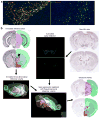
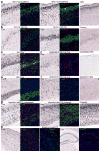
The Cre/lox system is widely used in mice to achieve cell-type-specific gene expression. However, a strong and universally responding system to express genes under Cre control is still lacking. We have generated a set of Cre reporter mice with strong, ubiquitous expression of fluorescent proteins of different spectra. The robust native fluorescence of these reporters enables direct visualization of fine dendritic structures and axonal projections of the labeled neurons, which is useful in mapping neuronal circuitry, imaging and tracking specific cell populations in vivo. Using these reporters and a high-throughput in situ hybridization platform, we are systematically profiling Cre-directed gene expression throughout the mouse brain in several Cre-driver lines, including new Cre lines targeting different cell types in the cortex. Our expression data are displayed in a public online database to help researchers assess the utility of various Cre-driver lines for cell-type-specific genetic manipulation.
Figures
References
-
- Feng G, et al. Imaging neuronal subsets in transgenic mice expressing multiple spectral variants of GFP. Neuron. 2000;28:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Sugino K, et al. Molecular taxonomy of major neuronal classes in the adult mouse forebrain. Nature neuroscience. 2006;9:99–107. - PubMed
-
- Zong H, Espinosa JS, Su HH, Muzumdar MD, Luo L. Mosaic analysis with double markers in mice. Cell. 2005;121:479–492. - PubMed
-
- Balthasar N, et al. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron. 2004;42:983–991. - PubMed
-
- Kellendonk C, et al. Transient and selective overexpression of dopamine D2 receptors in the striatum causes persistent abnormalities in prefrontal cortex functioning. Neuron. 2006;49:603–615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

