Topical delivery of silymarin constituents via the skin route
- PMID: 20023692
- PMCID: PMC4002699
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.186
Topical delivery of silymarin constituents via the skin route
Abstract
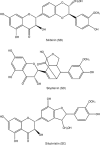
Aim: Silibinin (SB), silydianin (SD), and silychristin (SC) are components of silymarin. These compounds can be used to protect the skin from oxidative stress induced by ultraviolet (UV) irradiation and treat it. To this end, the absorption of silymarin constituents via the skin was examined in the present report.
Methods: Transport of SB, SD, and SC under the same thermodynamic activity through and into the skin and the effects of pH were studied in vitro using a Franz diffusion assembly.
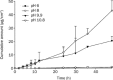
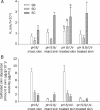
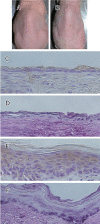
Results: The lipophilicity increased in the order of SC<SD<SB. Increased lipophilicity of a compound resulted in higher skin deposition but had a minor effect on permeation across the skin in the less-ionized form (pH 8). It is apparent that compounds in the less-ionized form showed higher skin uptake compared to the more-ionized form. Hyperproliferative skin produced by UVB exposure showed increased permeation of silymarin constituents in the less-ionized form, but it did not affect deposition within the skin. With in vivo topical application for 4 and 8 h, the skin deposition of SB was higher than those of SD and SC by 3.5 approximately 4.0- and 30 approximately 40-fold, respectively. The skin disruption and erythema test demonstrated that the topical application of these compounds for up to 24 h caused no apparent skin irritation.
Conclusion: The basic profiles of silymarin permeation via skin route were established.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A comparison of skin delivery of ferulic acid and its derivatives: evaluation of their efficacy and safety.Int J Pharm. 2010 Oct 31;399(1-2):44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.07.054. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Int J Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20692328
-
Skin Delivery of EGCG and Silibinin: Potential of Peptide Dendrimers for Enhanced Skin Permeation and Deposition.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017 Aug;18(6):2346-2357. doi: 10.1208/s12249-017-0718-0. Epub 2017 Jan 25. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017. PMID: 28124212
-
Development of silymarin topical formulation: In vitro and ex vivo dermal kinetics of silymarin.Int J Pharm. 2023 Jan 5;630:122431. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122431. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36436747
-
Drug-drug interactions of silymarin on the perspective of pharmacokinetics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jan 21;121(2):185-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.10.036. Epub 2008 Nov 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19041708 Review.
-
Biotransformation of silybin and its congeners.Curr Drug Metab. 2013 Dec;14(10):1009-21. doi: 10.2174/1389200214666131118234507. Curr Drug Metab. 2013. PMID: 24261705 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and in vivo percutaneous absorption of seleno-L-methionine, an antioxidant agent, and other selenium species.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Sep;32(9):1181-90. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.89. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 21785447 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advancements and Trends of Topical Drug Delivery Systems in Psoriasis: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jul 29;19:7631-7671. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S461514. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39099792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Antioxidants on Vitiligo and Melasma: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;12(12):2082. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122082. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136202 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Pre- and Post-Treatment by Topical Formulations Containing Dissolved and Suspended Silybum marianum against UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress in Guinea Pig and on HaCaT Keratinocytes.Molecules. 2016 Sep 22;21(10):1269. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101269. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27669200 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric Micelles: A Promising Pathway for Dermal Drug Delivery.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 28;14(23):7278. doi: 10.3390/ma14237278. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meeran SM, Katiyar S, Elmets CA, Katiyar SK. Silymarin inhibits UV radiation-induced immunosuppression through augmentation of interleukin-12 in mice. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:1660–8. - PubMed
-
- Dhanalakshmi S, Mallikarjuna GU, Singh RP, Agarwal R. Dual efficacy of silibinin in protecting or enhancing ultraviolet B radiation-caused apoptosis in HaCaT human immortalized keratinocytes. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:99–106. - PubMed
-
- Leiter U, Garbe C. Epidemiology of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer — the role of sunlight. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;624:89–103. - PubMed
-
- Ramos J, Villa J, Ruiz A, Armstrong R, Matta J. UV dose determines key characteristics of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13:2006–11. - PubMed
-
- Afaq F, Adhami VM, Mukhtar H. Photochemoprevention of ultraviolet B signaling and photocarcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 2005;571:153–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

