Unbiased discovery of in vivo imaging probes through in vitro profiling of nanoparticle libraries
- PMID: 20023731
- PMCID: PMC2748356
- DOI: 10.1039/b821775k
Unbiased discovery of in vivo imaging probes through in vitro profiling of nanoparticle libraries
Abstract
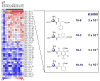
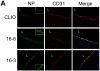
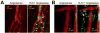
In vivo imaging reveals how proteins and cells function as part of complex regulatory networks in intact organisms, and thereby contributes to a systems-level understanding of biological processes. However, the development of novel in vivo imaging probes remains challenging. Most probes are directed against a limited number of pre-specified protein targets; cell-based screens for imaging probes have shown promise, but raise concerns over whether in vitro surrogate cell models recapitulate in vivo phenotypes. Here, we rapidly profile the in vitro binding of nanoparticle imaging probes in multiple samples of defined target vs. background cell types, using primary cell isolates. This approach selects for nanoparticles that show desired targeting effects across all tested members of a class of cells, and decreases the likelihood that an idiosyncratic cell line will unduly skew screening results. To adjust for multiple hypothesis testing, we use permutation methods to identify nanoparticles that best differentiate between the target and background cell classes. (This approach is conceptually analogous to one used for high-dimensionality datasets of genome-wide gene expression, e.g. to identify gene expression signatures that discriminate subclasses of cancer.) We apply this approach to the identification of nanoparticle imaging probes that bind endothelial cells, and validate our in vitro findings in human arterial samples, and by in vivo intravital microscopy in mice. Overall, this work presents a generalizable approach to the unbiased discovery of in vivo imaging probes, and may guide the further development of novel endothelial imaging probes.
Figures
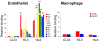

References
-
- Contag CH. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2006;16:633–54. ix. - PubMed
- Giepmans BN, Adams SR, Ellisman MH, Tsien RY. Science. 2006;312:217–224. - PubMed
- Sokolov K, Nida D, Descour M, Lacy A, Levy M, Hall B, Dharmawardhane S, Ellington A, Korgel B, Richards-Kortum R. Adv Cancer Res. 2007;96:299–344. - PubMed
- Weissleder R, Pittet MJ. Nature. 2008;452:580–589. - PMC - PubMed
- Kherlopian AR, Song T, Duan Q, Neimark MA, Po MJ, Gohagan JK, Laine AF. BMC Syst Biol. 2008;2:74. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nitin N, LaConte LE, Zurkiya O, Hu X, Bao G. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2004;9:706–712. - PubMed
- Schellenberger EA, Reynolds F, Weissleder R, Josephson L. Chembiochem. 2004;5:275–279. - PubMed
- Peng XH, Qian X, Mao H, Wang AY, Chen ZG, Nie S, Shin DM. Int J Nanomedicine. 2008;3:311–321. - PMC - PubMed
- Akerman ME, Chan WC, Laakkonen P, Bhatia SN, Ruoslahti E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:12617–12621. - PMC - PubMed
- Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RM, Chung LW, Nie S. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:969–976. - PubMed
- Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ, Sundaresan G, Wu AM, Gambhir SS, Weiss S. Science. 2005;307:538–544. - PMC - PubMed
- Wunderbaldinger P, Josephson L, Weissleder R. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13:264–268. - PubMed
-
- Joyce JA, Laakkonen P, Bernasconi M, Bergers G, Ruoslahti E, Hanahan D. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:393–403. - PubMed
-
- Rosania GR, Lee JW, Ding L, Yoon HS, Chang YT. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:1130–1131. - PubMed
- Li Q, Min J, Ahn YH, Namm J, Kim EM, Lui R, Kim HY, Ji Y, Wu H, Wisniewski T, Chang YT. Chembiochem. 2007;8:1679–1687. - PubMed
- Wagner BK, Carrinski HA, Ahn YH, Kim YK, Gilbert TJ, Fomina DA, Schreiber SL, Chang YT, Clemons PA. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:4208–4209. - PubMed
-
- Weissleder R, Kelly K, Sun EY, Shtatland T, Josephson L. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1418–1423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

