Electrically evoking and electrochemically resolving quantal release on a microchip
- PMID: 20024047
- PMCID: PMC3000936
- DOI: 10.1039/b911763f
Electrically evoking and electrochemically resolving quantal release on a microchip
Abstract
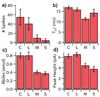
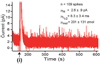
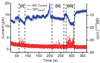
A microchip was applied to electrically depolarize rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells and to simultaneously detect exocytotic catecholamine release amperometrically. Results demonstrate exocytosis elicited by flowing cells through an electric field generated by a potentiostat circuit in a microchannel, as well as exocytosis triggered by application of an extracellular voltage pulse across. Electrical finite element model (FEM) analysis illustrated that larger cells experienced greater depolarizing excitation from the extracellular electric fields due to the smaller shunt path and higher resistance to current flow in the channel around the cell. Consistent with these simulations, data recorded from cell clusters and large cells exhibited increased release rates relative to data from the smaller cells. Overall, the system was capable of resolving single vesicle quantal release, in the zeptomole range, as well as the kinetics associated with the vesicle fusion process. Analysis of spike population statistics suggested detection of catecholamines from multiple release sites around the cells. The potential for such a device to be used in flow cytometry to evoke and detect exocytosis was demonstrated.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Magnetron sputtered diamond-like carbon microelectrodes for on-chip measurement of quantal catecholamine release from cells.Biomed Microdevices. 2008 Oct;10(5):623-9. doi: 10.1007/s10544-008-9173-8. Biomed Microdevices. 2008. PMID: 18493856 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled on-chip stimulation of quantal catecholamine release from chromaffin cells using photolysis of caged Ca2+ on transparent indium-tin-oxide microchip electrodes.Lab Chip. 2008 Jan;8(1):161-9. doi: 10.1039/b715308m. Epub 2007 Oct 26. Lab Chip. 2008. PMID: 18094774 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated microchip system for the detection of quantal exocytosis from single and small ensembles of cells.Lab Chip. 2008 Feb;8(2):323-9. doi: 10.1039/b715107a. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Lab Chip. 2008. PMID: 18231673
-
Microchip-based electrochemical detection for monitoring cellular systems.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 Apr;405(10):3013-20. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6682-3. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23340999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical measurement of quantal exocytosis using microchips.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Jan;470(1):97-112. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2063-2. Epub 2017 Sep 2. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 28866728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
All-carbon multi-electrode array for real-time in vitro measurements of oxidizable neurotransmitters.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 9;6:20682. doi: 10.1038/srep20682. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26857940 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic platforms for single neuron analysis.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Feb 16;13:100222. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100222. eCollection 2022 Jan. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35243297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous distribution of exocytotic microdomains in adrenal chromaffin cells resolved by high-density diamond ultra-microelectrode arrays.J Physiol. 2014 Aug 1;592(15):3215-30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.274951. Epub 2014 May 30. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24879870 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterization of a diamond-insulated graphitic multi electrode array realized with ion beam lithography.Sensors (Basel). 2014 Dec 30;15(1):515-28. doi: 10.3390/s150100515. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25558992 Free PMC article.
-
Automated targeting of cells to electrochemical electrodes using a surface chemistry approach for the measurement of quantal exocytosis.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2010 Jul 1;1(9):590-597. doi: 10.1021/cn1000183. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21113333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knight DE, Tonge DA, Baker PF. Nature. 1985;317:719–721. - PubMed
-
- Edwardson JM, Wang C-T, Gong B, Wyttenbach A, Bai J, Jackson MB, Chapman ER, Morton AJ. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:30849–30853. - PubMed
-
- Keating DJ, Dubach D, Zanin MP, Yu Y, Martin K, Zhao Y-F, Chen C, Porta S, Arbone’s ML, Mittaz L, Pritchard MA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008;17:1020–1030. - PubMed
-
- Chen TK, Luo G, Ewing AG. Anal. Chem. 1994;66:3031–3035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

