Sulfated, low-molecular-weight lignins are potent inhibitorsof plasmin, in addition to thrombin and factor Xa: Novel opportunity for controlling complex pathologies
- PMID: 20024500
- PMCID: PMC4080834
- DOI: 10.1160/TH09-07-0454
Sulfated, low-molecular-weight lignins are potent inhibitorsof plasmin, in addition to thrombin and factor Xa: Novel opportunity for controlling complex pathologies
Abstract
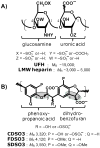
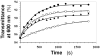
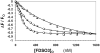
Recently we prepared sulfated, low-molecular-weight lignins (LMWLs) to mimic the biological activities of heparin and heparan sulfate. Chemo-enzymatically prepared sulfated LMWLs represent a library of diverse non-sugar, aromatic molecules with structures radically different from the heparins, and have been found to potently inhibit thrombin and factor Xa. To assess their effect on the fibrinolytic system, we studied the interaction of LMWLs with human plasmin. Enzyme inhibition studies indicate that the three sulfated LMWLs studied inhibit plasmin with IC50 values in the range of 0.24 and 1.3 mM, which are marginally affected in the presence of antithrombin. Similarly, plasmin degradation of polymeric fibrin is also inhibited by sulfated LMWLs. Michaelis-Menten kinetic studies indicate that maximal velocity of hydrolysis of chromogenic substrates decreases nearly 70% in the presence of LMWLs, while the effect on Michaelis constant is dependent on the nature of the substrate. Competitive binding studies indicate that the sulfated LMWLs compete with full-length heparin. Comparison with thrombin-heparin crystal structure identifies an anionic region on plasmin as a plausible sulfated LMWL binding site. Overall, the chemo-enzymatic origin coupled with coagulation and fibrinolysis inhibition properties of sulfated LMWLs present novel opportunities for designing new pharmaceutical agents that regulate complex pathologies in which both systems are known to play important roles such as disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Figures

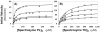
Similar articles
-
Sulfated, low molecular weight lignins inhibit a select group of heparin-binding serine proteases.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jan 6;417(1):382-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.122. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22155248 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfated low molecular weight lignins, allosteric inhibitors of coagulation proteinases via the heparin binding site, significantly alter the active site of thrombin and factor xa compared to heparin.Thromb Res. 2014 Nov;134(5):1123-9. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.08.024. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Thromb Res. 2014. PMID: 25242245 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmin regulation through allosteric, sulfated, small molecules.Molecules. 2015 Jan 5;20(1):608-24. doi: 10.3390/molecules20010608. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25569517 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin inhibitors as antithrombotic agents: the importance of rapid inhibition.J Enzyme Inhib. 1995;9(1):3-15. doi: 10.3109/14756369509040677. J Enzyme Inhib. 1995. PMID: 8568565 Review.
-
Low molecular weight heparins: antithrombotic and haemorrhagic effects and standardization.Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1988;543:57-64. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1988. PMID: 2847459 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Orally Active Thrombin Inhibitors for the Treatment of Thrombotic Disorder Diseases.Molecules. 2015 Jun 15;20(6):11046-62. doi: 10.3390/molecules200611046. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26083038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfated Non-Saccharide Glycosaminoglycan Mimetics as Novel Drug Discovery Platform for Various Pathologies.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(21):3412-3447. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666181120101147. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30457046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric Partial Inhibition of Monomeric Proteases. Sulfated Coumarins Induce Regulation, not just Inhibition, of Thrombin.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 7;6:24043. doi: 10.1038/srep24043. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27053426 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfated, low molecular weight lignins inhibit a select group of heparin-binding serine proteases.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jan 6;417(1):382-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.122. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22155248 Free PMC article.
-
Designing Smaller, Synthetic, Functional Mimetics of Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans as Allosteric Modulators of Coagulation Factors.J Med Chem. 2023 Apr 13;66(7):4503-4531. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00132. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37001055 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gandhi NS, Mancera RL. The structure of glycosaminoglycans and their interactions with proteins. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008;72:455–482. - PubMed
-
- Capila I, Linhardt RJ. Heparin-protein interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002;41:391–412. - PubMed
-
- Esko JD, Selleck SB. Order out of chaos: Assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:435–471. - PubMed
-
- Rabenstein DL. Heparin and heparan sulfate: structure and function. Nat Prod Rep. 2002;19:312–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

