Evidence for cross-talk between atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide receptors
- PMID: 20024606
- PMCID: PMC2863078
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-009-0352-6
Evidence for cross-talk between atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide receptors
Abstract
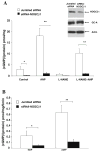
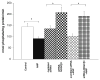
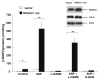
Guanylyl cyclases (GCs), a ubiquitous family of enzymes that metabolize GTP to cyclic GMP (cGMP), are traditionally divided into membrane-bound forms (GC-A-G) that are activated by peptides and cytosolic forms that are activated by nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide. However, recent data has shown that NO activated GC's (NOGC) also may be associated with membranes. In the present study, interactions of guanylyl cyclase A (GC-A), a caveolae-associated, membrane-bound, homodimer activated by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), with NOGC, a heme-containing heterodimer (alpha/beta) beta1 isoform of the beta subunit of NOGC (NOGCbeta1) was specifically focused. NOGCbeta1 co-localized with GC-A and caveolin on the membrane in human kidney (HK-2) cells. Interaction of GC-A with NOGCbeta1 was found using immunoprecipitations. In a second set of experiments, the possibility that NOGCbeta1 regulates signaling by GC-A in HK-2 cells was explored. ANP-stimulated membrane guanylyl cyclase activity (0.05 +/- 0.006 pmol/mg protein/5 min; P < 0.01) and intra cellular GMP (18.1 +/- 3.4 vs. 1.2 +/- 0.5 pmol/mg protein; P < 0.01) were reduced in cells in which NOGCbeta1 abundance was reduced using specific siRNA to NOGCbeta1. On the other hand, ANP-stimulated cGMP formation was increased in cells transiently transfected with NOGCbeta1 (530.2 +/- 141.4 vs. 26.1 +/- 13.6 pmol/mg protein; P < 0.01). siRNA to NOGCbeta1 attenuated inhibition of basolateral Na/K ATPase activity by ANP (192 +/- 22 vs. 92 +/- 9 nmol phosphate/mg protein/min; P < 0.05). In summary, the results show that NOGCbeta1 and GC-A interact and that NOGCbeta1 regulates ANP signaling in HK-2 cells. The results raise the novel possibility of cross-talk between NOGC and GC-A signaling pathways in membrane caveolae.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 is a novel cellular target of atrial natriuretic peptide signaling in renal epithelial cells.Cell Signal. 2012 May;24(5):1100-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22285803 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide signaling antagonizes vasopressin-mediated water permeability in inner medullary collecting duct cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Sep;297(3):F693-703. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00136.2009. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19570884
-
Natriuretic peptides stimulate the cardiac sodium pump via NPR-C-coupled NOS activation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Apr;294(4):C1067-73. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00243.2007. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18272821
-
[Structure, regulation and functions of particulate guanylyl cyclase type A].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Apr 9;69:457-68. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1148746. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 25897107 Review. Polish.
-
Regulation and therapeutic targeting of peptide-activated receptor guanylyl cyclases.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Apr;130(1):71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.12.005. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21185863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-specific differences in natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide synthase expression in ANP gene-disrupted mice.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Feb;374(1-2):125-35. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1511-8. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23180242
-
Neutrophil-Initiated Myocardial Inflammation and Its Modulation by B-Type Natriuretic Peptide: A Potential Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 31;20(1):129. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010129. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30602672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac-specific overexpression of caveolin-3 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy and increases natriuretic peptide expression and signaling.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 May 31;57(22):2273-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.12.032. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21616289 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 is a novel cellular target of atrial natriuretic peptide signaling in renal epithelial cells.Cell Signal. 2012 May;24(5):1100-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22285803 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of microRNAs in atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):C929-37. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00088.2011. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21734186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lucas KA, Pitari GM, Kazerounian S, Ruiz-Stewart I, Park J, Schulz S, Chepenik KP, Waldman SA. Guanylyl cyclases and signaling by cyclic GMP. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:375–414. - PubMed
-
- Foster DC, Wedel BJ, Robinson SW, Garbers DL. Mechanisms of regulation and functions of guanylyl cyclases. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;135:1–39. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn M. Structure, regulation, and function of mammalian membrane guanylyl cyclase receptors, with a focus on guanylyl cyclase-A. Circ Res. 2003;93:700–709. - PubMed
-
- Ruskoaho H. Atrial natriuretic peptide: synthesis, release, and metabolism. Pharmacol Rev. 1992;44:479–602. - PubMed
-
- Wilson EM, Chinkers M. Identification of sequences mediating guanylyl cyclase dimerization. Biochemistry. 1995;34:4696–4701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

