Epitope analysis of peanut allergen Ara h1 with human monoclonal IgM antibody 92-2
- PMID: 20024620
- PMCID: PMC2978308
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-009-9243-7
Epitope analysis of peanut allergen Ara h1 with human monoclonal IgM antibody 92-2
Abstract
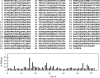
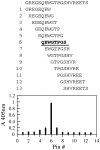
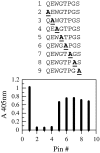
A human-mouse hybridoma clone 92-2 secreting IgM-class human monoclonal antibody to peanut allergen protein Ara h1 was established. To detect antibody-binding sequences on Ara h1, we synthesized a series of peptides of the Ara h1 protein on a multi-pin apparatus for the pin-peptide ELISA. The 92-2 human monoclonal antibody was found to recognize a sequence of GREGEQEWGTPGSHVREETS. Further analysis with shorter pin-peptides with eight amino acid-long showed that the sequence of QEWGTPGS was an essential linear sequence of this epitope. When the QEW part of the sequence was replaced by alanine, the 92-2 monoclonal antibody did not bind to the substituted peptide, showing that those amino acids play an important role in the binding of the 92-2 monoclonal antibody.
Figures
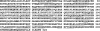
Similar articles
-
Epitope analysis of peanut allergen Ara h1 with human monoclonal IgM antibody clone #86.Hum Antibodies. 2010;19(4):101-5. doi: 10.3233/HAB-2010-0233. Hum Antibodies. 2010. PMID: 21178281
-
Generation of mouse-human hybridomas secreting antibodies against peanut allergen Ara h1.Cytotechnology. 2004 Sep;46(1):19-23. doi: 10.1007/s10616-005-1578-0. Epub 2005 Jun 16. Cytotechnology. 2004. PMID: 19003255 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope analysis of Japanese cedar pollen allergen Cry j1 with the human monoclonal antibody 4701-1.Hum Antibodies. 2013;22(3-4):73-6. doi: 10.3233/HAB-140273. Hum Antibodies. 2013. PMID: 24961865
-
Epitope analysis of Japanese cedar pollen allergen Cry j2 with a human IgM class monoclonal antibody 404-117.Hum Antibodies. 2017;25(1-2):17-21. doi: 10.3233/HAB-160301. Hum Antibodies. 2017. PMID: 27858705
-
Epitope analysis of peanut allergen Ara h1 with oligoclonal IgM antibody from human B-lymphoblastoid cells.Cytotechnology. 2008 Jun;57(2):177-80. doi: 10.1007/s10616-008-9142-3. Epub 2008 Apr 11. Cytotechnology. 2008. PMID: 19003163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burks AW, Shin D, Cockrell G, Stanley JS, Helm RM, Bannon GA. Mapping and mutational analysis of the IgE-binding epitopes on Ara h 1, a legume vicilin protein and a major allergen in peanut hypersensitivity. Eur J Biochem. 1997;245:334–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00334.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crain MJ, Sanders SK, Butler JL, Cooper MD. Epstein-Barr virus preferentially induces proliferation of primed B cells. J Immunol. 1989;143:1543–1548. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

