Effects of acute nitric oxide synthase inhibition on lower leg vascular function in chronic tetraplegia
- PMID: 20025149
- PMCID: PMC2792459
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2009.11754555
Effects of acute nitric oxide synthase inhibition on lower leg vascular function in chronic tetraplegia
Abstract
Background/objective: To improve our understanding of the lower-leg vascular responses of nitric oxide synthase inhibition in persons with tetraplegia.
Participants: Six people with chronic tetraplegia and 6 age-matched controls.
Methods: Lower-leg relative vascular resistance and venous volume variation were obtained by venous occlusion plethysmography and blood pressure by auscultation at baseline. Postintravenous infusion of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine-methyl-ester (1 mg x kg(-1) or placebo on separate days.
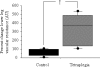
Results: At baseline in the group with tetraplegia compared with controls, mean arterial pressure and relative vascular resistance of the leg were significantly lower. After nitric oxide synthase inhibition, mean arterial pressure and lower leg vascular resistance were significantly elevated in both groups. There were no group or intervention differences in venous volume variation.
Conclusion: These preliminary results suggest that nitric oxide synthase inhibition with 1 mg x kg(-1) N(G)-nitro-L-arginine-methyl-ester normalizes seated blood pressure and lower leg vascular resistance to control group baseline levels.
Figures


References
-
- Teasell RW, Arnold JM, Krassioukov A, Delaney GA. Cardiovascular consequences of loss of supraspinal control of the sympathetic nervous system after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000;81(4):506–516. - PubMed
-
- Guizar-Sahagun G, Castaneda-Hernandez G, Garcia-Lopez P, Franco-Bourland R, Grijalva I, Madrazo I. Pathophysiological mechanisms involved in systemic and metabolic alterations secondary to spinal cord injury. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1998;41:237–240. - PubMed
-
- Claus-Walker J, Halstead LS. Metabolic and endocrine changes in spinal cord injury: II (section 1). Consequences of partial decentralization of the autonomic nervous system. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1982;63(11):569–575. - PubMed
-
- Munakata M, Kameyama J, Nunokawa T, Ito N, Yoshinaga K. Altered Mayer wave and baroreflex profiles in high spinal cord injury. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14(2):141–148. - PubMed
-
- Mathias CJ, Christensen NJ, Corbett JL, Frankel HL, Goodwin TJ, Peart WS. Plasma catecholamines, plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone in tetraplegic man, horizontal and tilted. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975;49(4):291–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
