Anti-arthritic effects and toxicity of the essential oils of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.)
- PMID: 20025215
- PMCID: PMC2834817
- DOI: 10.1021/jf9027206
Anti-arthritic effects and toxicity of the essential oils of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.)
Abstract
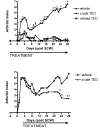
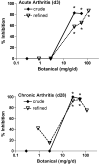
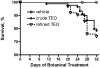
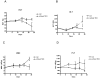
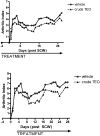
Turmeric (Curcuma longa L., Zingiberaceae) rhizomes contain two classes of secondary metabolites, curcuminoids and the less well-studied essential oils. Having previously identified potent anti-arthritic effects of the curcuminoids in turmeric extracts in an animal model of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), studies were undertaken to determine whether the turmeric essential oils (TEO) were also joint protective using the same experimental model. Crude or refined TEO extracts dramatically inhibited joint swelling (90-100% inhibition) in female rats with streptococcal cell wall (SCW)-induced arthritis when extracts were administered via intraperitoneal injection to maximize uniform delivery. However, this anti-arthritic effect was accompanied by significant morbidity and mortality. Oral administration of a 20-fold higher dose TEO was nontoxic, but only mildly joint-protective (20% inhibition). These results do not support the isolated use of TEO for arthritis treatment but, instead, identify potential safety concerns in vertebrates exposed to TEO.
Figures

References
-
- Pichersky E, Gang DR. Genetics and biochemistry of secondary metabolites in plants: an evolutionary perspective. Trends Plant Sci. 2000;5:439–445. - PubMed
-
- Lantz RC, Chen GJ, Solyom AM, Jolad SD, Timmermann BN. The effect of turmeric extracts on inflammatory mediator production. Phytomedicine. 2005;12:445–452. - PubMed
-
- Funk JL, Frye JB, Oyarzo JN, Kuscuoglu N, Wilson J, McCaffrey G, Stafford G, Chen G, Lantz RC, Jolad SD, Solyom AM, Kiela PR, Timmermann BN. Efficacy and mechanism of action of turmeric supplements in the treatment of experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3452–3464. - PubMed
-
- Chainani-Wu N. Safety and anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin: a component of tumeric (Curcuma longa) J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2003;9:161–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

