Regulation of mRNA cap methylation
- PMID: 20025612
- PMCID: PMC2825737
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20091352
Regulation of mRNA cap methylation
Abstract
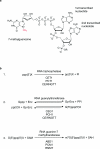
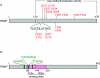
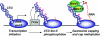
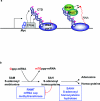
The 7-methylguanosine cap added to the 5' end of mRNA is essential for efficient gene expression and cell viability. Methylation of the guanosine cap is necessary for the translation of most cellular mRNAs in all eukaryotic organisms in which it has been investigated. In some experimental systems, cap methylation has also been demonstrated to promote transcription, splicing, polyadenylation and nuclear export of mRNA. The present review discusses how the 7-methylguanosine cap is synthesized by cellular enzymes, the impact that the 7-methylguanosine cap has on biological processes, and how the mRNA cap methylation reaction is regulated.
Figures
References
-
- Shuman S. What messenger RNA capping tells us about eukaryotic evolution. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002;3:619–625. - PubMed
-
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976;9:645–653. - PubMed
-
- Shibagaki Y., Itoh N., Yamada H., Nagata S., Mizumoto K. mRNA capping enzyme. Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding mRNA guanylytransferase subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:9521–9528. - PubMed
-
- Tsukamoto T., Shibagaki Y., Imajoh-Ohmi S., Murakoshi T., Suzuki M., Nakamura A., Gotoh H., Mizumoto K. Isolation and characterization of the yeast mRNA capping enzyme beta subunit gene encoding RNA 5′-triphosphatase, which is essential for cell viability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997;239:116–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

